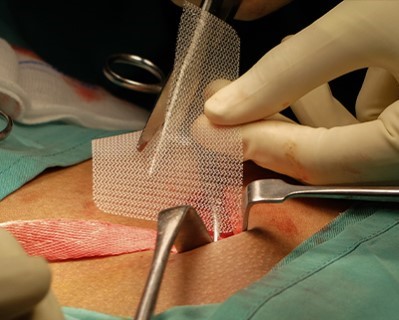
Hernia Repair
- Purpose: Repairs hernias to prevent complications and relieve symptoms.
- Procedure: The protruding tissue is pushed back into place and the weakened area is reinforced with mesh.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to routine Hernia Repair procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and location of the hernia, patient tolerance, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health and the complexity of the surgery can also influence the recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Hernia repair is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, meaning most patients can return home the same day after a short observation period. However, in cases of complex or recurrent hernias, or if complications arise, an overnight hospital stay may be required for closer monitoring.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing hernia repair usually do not require an overnight hospital stay and can be discharged within a few hours after the procedure, once they are fully awake and stable. If an open hernia repair or a more complex procedure is performed, a hospital stay of 1 to 2 days may be necessary.Type of Anesthesia
Hernia repair can be performed under general anesthesia, local anesthesia with sedation, or spinal anesthesia, depending on the type of hernia, the complexity of the surgery, and the patient’s preference. General anesthesia is more common for laparoscopic repairs, while local or spinal anesthesia may be used for simpler, open procedures.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel, particularly long-distance or air travel, for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure. This allows time for initial recovery and monitoring for any potential complications, such as infection or recurrence of the hernia. Patients should follow specific recommendations from their healthcare provider regarding travel and activity levels based on their recovery progress.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for hernia repair involves following specific guidelines provided by the healthcare provider. Patients may be advised to avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the surgery, typically after midnight the night before the procedure. It is also important to inform the surgical team of any medications the patient is taking, particularly blood thinners, as these may need to be adjusted before surgery. Pre-operative tests, such as blood work and imaging studies, may be required to assess the hernia and plan the surgery.Procedure Duration
The hernia repair procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the hernia and the type of repair (laparoscopic or open). During the surgery, the surgeon pushes the protruding tissue back into place and repairs the weakness in the muscle or abdominal wall, often reinforcing the area with a synthetic mesh to prevent recurrence. Laparoscopic surgery involves small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments, while open surgery involves a larger incision to access and repair the hernia.Recovery Time
Recovery from hernia repair varies depending on the type of surgery performed. For laparoscopic hernia repair, most patients can resume light activities within a few days and return to work within 1 to 2 weeks. For open hernia repair, recovery may take longer, with patients typically needing 4 to 6 weeks to fully recover. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and bending over during the recovery period to prevent strain on the repair site. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions on activity restrictions and attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of hernia repair can vary depending on the surgeon's expertise, the complexity of the procedure (laparoscopic vs. open), and geographic location. Insurance coverage may also affect the out-of-pocket cost. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or surgical center directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for hernia repair involves managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper healing. Patients are usually prescribed pain relievers and may be given antibiotics to prevent infection. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions on how to care for the surgical incisions, including keeping them clean and dry. Patients should also be aware of potential complications, such as infection, bleeding, or hernia recurrence, and seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise. A follow-up appointment is typically scheduled within a few weeks to assess the healing process and address any questions or concerns.