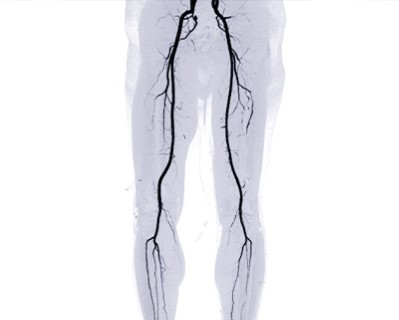
Peripheral Angiography
- Purpose: Diagnoses peripheral artery disease by visualizing blood flow in the peripheral arteries.
- Procedure: Similar to coronary angiography, but focuses on arteries outside the heart, such as in the legs.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Peripheral Angiography procedures without extraordinary circumstances. However, specifics may vary based on individual patient factors, such as the extent of peripheral artery disease, the presence of other vascular conditions, or complications that might arise during the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the need for additional interventions, or the complexity of the angiography can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Peripheral Angiography is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day. However, if the procedure reveals significant blockages that require immediate intervention, or if complications arise, a hospital stay might be necessary for further treatment and observation.Hospital Stay Duration
Most patients undergoing Peripheral Angiography are monitored for a few hours after the procedure and can usually be discharged on the same day. If additional treatments, such as angioplasty or stent placement, are performed during the same session, an overnight stay might be required to ensure the patient’s condition remains stable.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia at the catheter insertion site, often in the groin or arm. Mild sedation may also be administered to help the patient relax during the procedure. General anesthesia is rarely used but may be considered in specific cases depending on the patient’s condition.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel for at least 24 hours after Peripheral Angiography, particularly if sedation was used. Depending on the findings and any additional procedures performed, longer or more strenuous travel may be postponed for a few days to ensure the patient is stable and comfortable.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients are typically instructed to fast for several hours. They may also need to temporarily stop taking certain medications, particularly blood thinners, as directed by their healthcare provider to reduce the risk of bleeding during the procedure.Procedure Duration
Peripheral Angiography usually takes about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the extent of the vascular examination and whether any additional interventions are performed during the procedure.Recovery Time
Most patients can resume light activities within a day or two after the procedure. However, it is recommended to avoid strenuous activities for several days, particularly those that could put stress on the catheter insertion site.Estimated Cost
The cost of Peripheral Angiography can vary depending on the hospital, geographic location, and whether any additional procedures, such as angioplasty or stenting, are performed. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care involves monitoring the catheter insertion site for signs of infection, bleeding, or swelling. Patients will also need to follow up with their healthcare provider to review the results of the angiography and discuss any further treatment or lifestyle changes needed. If additional interventions were performed, regular follow-ups may be necessary to monitor vascular health and the effectiveness of the treatment.