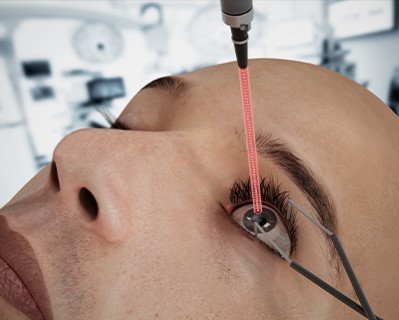
Photocoagulation
- Purpose: Treats various retinal disorders by sealing or destroying abnormal blood vessels.
- Procedure: A laser is used to create small burns on the retina.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Photocoagulation procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the underlying eye condition being treated, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Photocoagulation is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing photocoagulation do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
Photocoagulation is performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. The procedure is generally quick and minimally invasive.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow for proper monitoring and to address any potential complications, such as eye discomfort or vision changes.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for photocoagulation involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before the procedure, and arranging for transportation home after the treatment. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The photocoagulation procedure typically lasts about 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the extent of treatment needed. The ophthalmologist uses a laser to create small burns on the retina, which helps to seal leaking blood vessels or reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in conditions such as diabetic retinopathy.Recovery Time
Recovery from photocoagulation is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, redness, or blurred vision immediately following the procedure, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days.Estimated Cost
The cost of photocoagulation can vary depending on the extent of treatment, the ophthalmologist's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for photocoagulation includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Patients should monitor for any signs of complications, such as increased pain, severe redness, or changes in vision, and report these to their healthcare provider immediately. Regular follow-up appointments are important to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and determine if additional sessions are needed.