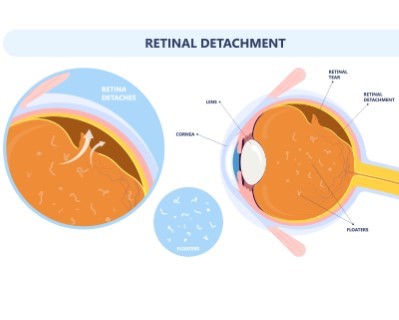
Retinal Detachment Surgery
- Purpose: Reattaches the retina to prevent vision loss.
- Procedure: Techniques include pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckle, and vitrectomy.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Retinal Detachment Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the detachment, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Retinal detachment surgery can be performed as either an inpatient or outpatient procedure, depending on the complexity of the detachment and the specific surgical method used.Hospital Stay Duration
For less complex cases, patients may be discharged the same day after the surgery. However, more complex surgeries may require an overnight hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation, ensuring the patient is comfortable and pain-free. In more complex cases, general anesthesia may be required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 2 to 4 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as increased eye pressure or recurrence of the detachment. If a gas bubble is used in the eye during surgery, air travel is contraindicated until the bubble has fully absorbed.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for retinal detachment surgery involves following specific guidelines from the ophthalmologist, such as fasting before surgery if sedation or general anesthesia is planned, using prescribed eye drops, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The duration of retinal detachment surgery varies depending on the severity of the detachment and the method used but generally lasts between 1 to 3 hours. Surgical techniques may include scleral buckling, vitrectomy, or pneumatic retinopexy, depending on the specific needs of the patient.Recovery Time
Recovery from retinal detachment surgery can take several weeks to a few months. During the initial recovery period, patients may need to maintain specific head positions, especially if a gas bubble was used during surgery. Full stabilization of vision can take time, and patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sudden head movements during recovery.Estimated Cost
The cost of retinal detachment surgery can vary based on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for retinal detachment surgery includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and manage eye pressure. Patients must adhere to all post-surgery instructions, including maintaining specific head positions if a gas bubble was used. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and ensure the retina remains attached. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, vision changes, or signs of detachment recurrence, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately. Air travel is strictly prohibited if a gas bubble was used until it has completely absorbed, which can take several weeks.