Urology Treatments
_20240721201853608822__0.webp)
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
- Purpose: Treats urinary problems due to an enlarged prostate.
- Procedure: A resectoscope is inserted through the urethra to remove parts of the prostate.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size of the prostate, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
TURP is typically performed as an inpatient procedure, requiring a short hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing TURP generally require a hospital stay of 1 to 3 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor urinary function, manage pain, and prevent complications such as bleeding or infection.Type of Anesthesia
TURP is usually performed under spinal anesthesia, which numbs the lower half of the body. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for TURP involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work and urinalysis. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The TURP procedure typically lasts between 60 to 90 minutes. During the surgery, the surgeon inserts a resectoscope through the urethra to remove excess prostate tissue that is obstructing urine flow, thereby relieving symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).Recovery Time
Recovery from TURP can take several weeks. Most patients can resume light activities within 1 to 2 weeks, but full recovery, including the resolution of urinary symptoms, may take up to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sexual activity during the initial recovery period to prevent complications.Estimated Cost
The cost of TURP can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for TURP includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper urinary function. Patients may have a catheter in place for a few days after the surgery to help drain the bladder. They should follow their surgeon’s instructions for catheter care, wound care, and activity restrictions. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or difficulty urinating, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Radical Prostatectomy
- Purpose: Removes the prostate gland to treat prostate cancer.
- Procedure: The prostate gland and some surrounding tissue are surgically removed.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Radical Prostatectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the stage of prostate cancer, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Radical prostatectomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to its complexity, requiring a hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing radical prostatectomy generally require a hospital stay of 2 to 4 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor urinary function, manage pain, and prevent complications such as bleeding or infection.Type of Anesthesia
Radical prostatectomy is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, or pain.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for radical prostatectomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work, imaging, and possibly a biopsy. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The radical prostatectomy procedure typically lasts between 2 to 4 hours. During the surgery, the surgeon removes the entire prostate gland, along with some surrounding tissue and lymph nodes, to treat prostate cancer. The surgery can be performed using traditional open surgery, laparoscopic techniques, or robotic-assisted methods, depending on the patient’s situation and the surgeon’s expertise.Recovery Time
Recovery from radical prostatectomy can take several weeks to months. Most patients can begin light activities within 2 to 4 weeks, but full recovery, including regaining urinary control and sexual function, may take up to 6 months or longer. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sexual activity during the initial recovery period to prevent complications.Estimated Cost
The cost of radical prostatectomy can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgical method used, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for radical prostatectomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper urinary function. Patients may have a catheter in place for 1 to 2 weeks after the surgery to help drain the bladder. They should follow their surgeon’s instructions for catheter care, wound care, and activity restrictions. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess PSA levels, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, difficulty urinating, or blood in the urine, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
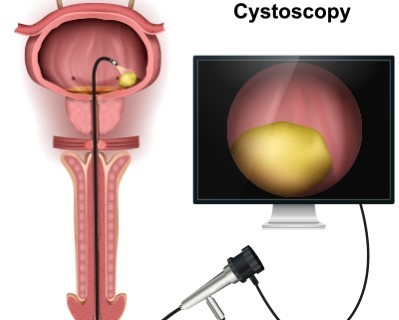
Cystoscopy
- Purpose: Diagnoses and treats conditions inside the bladder and urethra.
- Procedure: A cystoscope is inserted through the urethra to examine the bladder and urethra.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Cystoscopy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the presence of bladder abnormalities, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Cystoscopy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the procedure is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing cystoscopy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once the treatment is complete and they have recovered from any sedation.Type of Anesthesia
Cystoscopy is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the urethra and bladder to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. In some cases, light sedation or general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient's condition and the type of cystoscopy being performed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort, bleeding, or urinary issues.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for cystoscopy involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as drinking plenty of fluids before the procedure, avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, and arranging for transportation home if sedation or general anesthesia is used. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The cystoscopy procedure typically lasts between 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the purpose of the procedure and the findings. The healthcare provider inserts a thin, flexible tube with a camera (cystoscope) through the urethra into the bladder to examine the urinary tract and diagnose or treat bladder conditions.Recovery Time
Recovery from cystoscopy is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities immediately after the procedure. Some patients may experience minor discomfort, burning during urination, or a small amount of blood in the urine, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. It’s important to drink plenty of water to help flush the bladder and reduce irritation.Estimated Cost
The cost of cystoscopy can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, whether any treatments or biopsies are performed during the procedure, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care or lab tests.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for cystoscopy includes monitoring for any signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or worsening pain, and ensuring proper hydration to flush the bladder. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking pain relievers or antibiotics if prescribed. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary if any abnormalities were found during the procedure. Any signs of complications, such as difficulty urinating, severe pain, or persistent blood in the urine, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240721203252473967__0.webp)
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
- Purpose: Breaks kidney stones into smaller pieces that can be passed in the urine.
- Procedure: Shock waves are directed at the kidney stones to break them into smaller pieces.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of kidney stones, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
ESWL is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing ESWL generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from any sedation or anesthesia.Type of Anesthesia
ESWL is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation to keep the patient comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s preference and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain or difficulty passing fragments of the stone.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for ESWL involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if anesthesia is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The ESWL procedure typically lasts between 45 minutes to 1 hour. During the procedure, shock waves are directed at the kidney stones from outside the body, breaking them into smaller fragments that can be passed more easily through the urinary tract.Recovery Time
Recovery from ESWL is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, bruising, or blood in the urine, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. Patients are encouraged to drink plenty of water to help flush out stone fragments and may be advised to strain their urine to collect any fragments for analysis.Estimated Cost
The cost of ESWL can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the size and number of stones being treated, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care or imaging studies to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for ESWL includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or difficulty urinating. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking pain relievers, antibiotics, or medications to help pass stone fragments. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure that the stones have been completely cleared from the urinary tract. Any signs of complications, such as persistent pain or blood in the urine, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
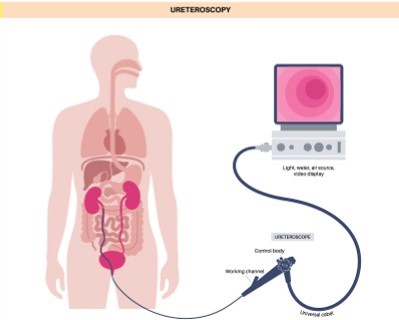
Ureteroscopy
- Purpose: Diagnoses and treats problems in the ureters and kidneys.
- Procedure: A ureteroscope is inserted through the bladder and ureter to visualize and treat the area.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Ureteroscopy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of kidney stones or ureteral strictures, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Ureteroscopy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing ureteroscopy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from any sedation or anesthesia.Type of Anesthesia
Ureteroscopy is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, local anesthesia with sedation may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, bleeding, or difficulty urinating.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for ureteroscopy involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if anesthesia is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The ureteroscopy procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the case. During the procedure, the healthcare provider inserts a thin, flexible tube (ureteroscope) through the urethra and bladder into the ureter to locate and remove kidney stones or treat ureteral strictures.Recovery Time
Recovery from ureteroscopy is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, blood in the urine, or frequent urination, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. Drinking plenty of water is recommended to help flush out any remaining stone fragments or debris.Estimated Cost
The cost of ureteroscopy can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the size and number of stones or strictures being treated, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care or imaging studies to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for ureteroscopy includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or difficulty urinating. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking pain relievers, antibiotics, or medications to help pass any remaining stone fragments. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure that the urinary tract is clear and healing properly. Any signs of complications, such as persistent pain, blood in the urine, or urinary retention, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
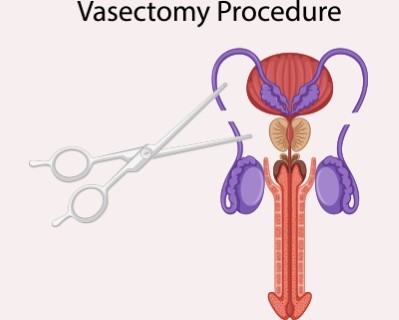
Vasectomy
- Purpose: Permanent male sterilization to prevent pregnancy.
- Procedure: The vas deferens are cut and sealed to prevent sperm from reaching the semen.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Vasectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s overall health and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Vasectomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the procedure is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing vasectomy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once they have recovered from any sedation.Type of Anesthesia
Vasectomy is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the scrotal area to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. In some cases, light sedation may be used, depending on the patient’s preference and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or swelling.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for vasectomy involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding and arranging for transportation home after the procedure if sedation is used. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The vasectomy procedure typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes. During the procedure, the healthcare provider makes small incisions or punctures in the scrotum to access and cut or seal the vas deferens, which blocks the sperm from mixing with the semen.Recovery Time
Recovery from vasectomy is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, bruising, or swelling in the scrotal area, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days to a week. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and sexual activity for about a week to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of vasectomy can vary depending on the healthcare provider's expertise, the method used (traditional or no-scalpel), and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and semen analysis to confirm the success of the procedure.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for vasectomy includes monitoring the scrotal area for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or swelling. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include using ice packs to reduce swelling, wearing supportive underwear, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. A follow-up semen analysis is typically required a few months after the procedure to confirm that no sperm is present in the semen. Any signs of complications, such as prolonged pain or infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240721204002613392__0.webp)
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
- Purpose: Removes tumors from the bladder.
- Procedure: A resectoscope is inserted through the urethra to remove bladder tumors.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of the tumor, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
TURBT is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, although some patients may require an overnight stay for monitoring, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing TURBT generally do not require a prolonged hospital stay. They are usually discharged the same day or the following day, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
TURBT is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, regional anesthesia (spinal or epidural) may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as bleeding, pain, or difficulty urinating.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for TURBT involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work and imaging studies. Patients should also arrange for transportation home after the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The TURBT procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the size and number of tumors being removed. During the procedure, the healthcare provider inserts a resectoscope through the urethra into the bladder to visualize and remove the tumor tissue.Recovery Time
Recovery from TURBT is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a few days. However, patients may experience blood in the urine, frequent urination, or mild discomfort for several days after the procedure. It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for managing these symptoms and to drink plenty of fluids to flush the bladder.Estimated Cost
The cost of TURBT can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the size and number of tumors being treated, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care, pathology analysis, and potential repeat procedures.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for TURBT includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or difficulty urinating. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include avoiding strenuous activities, using pain relievers, and following a specific fluid intake regimen. Regular follow-up appointments and cystoscopic examinations are crucial to monitor for recurrence of bladder tumors and to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. Any signs of complications, such as persistent pain, heavy bleeding, or infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Orchiectomy
- Purpose: Removes one or both testicles to treat testicular cancer or other conditions.
- Procedure: The testicle(s) are surgically removed through an incision in the scrotum.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Orchiectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the underlying reason for the procedure (e.g., cancer, trauma, or gender-affirming surgery), the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Orchiectomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing orchiectomy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Orchiectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, regional anesthesia (spinal or epidural) may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for orchiectomy involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work and imaging studies if necessary. Patients should also arrange for transportation home after the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The orchiectomy procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on whether one or both testicles are being removed. The surgeon makes an incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen, removes the testicle(s), and then closes the incision.Recovery Time
Recovery from orchiectomy is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a few days. However, patients may experience mild discomfort, bruising, or swelling in the surgical area, but these symptoms typically resolve within a week or two. It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for managing these symptoms, which may include wearing supportive underwear, using ice packs, and taking prescribed pain relievers.Estimated Cost
The cost of orchiectomy can vary depending on the reason for the surgery, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care, pathology analysis, and potential hormone replacement therapy if needed.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for orchiectomy includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or excessive swelling. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include activity restrictions, proper wound care, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing. If the orchiectomy was performed as part of cancer treatment, additional follow-up care and treatment may be necessary. Any signs of complications, such as fever, worsening pain, or abnormal discharge from the incision site, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
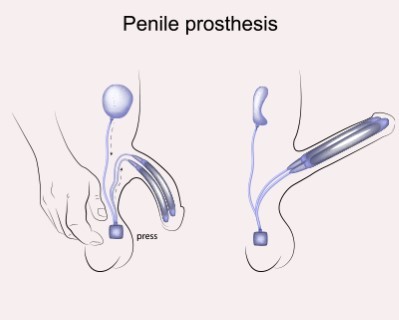
Penile Prosthesis Implantation
- Purpose: Treats erectile dysfunction by implanting a device to produce an erection.
- Procedure: A prosthetic device is surgically implanted into the penis.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Penile Prosthesis Implantation procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the type of prosthesis used, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Penile prosthesis implantation is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed. In some cases, an overnight stay may be required for monitoring.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing penile prosthesis implantation generally do not require a prolonged hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Penile prosthesis implantation is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, spinal or regional anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection, pain, or swelling.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for penile prosthesis implantation involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work and imaging studies. Patients should also arrange for transportation home after the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The penile prosthesis implantation procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the surgery, the surgeon places the prosthetic device within the penis through small incisions. The type of prosthesis (inflatable or semi-rigid) will determine the specific surgical technique used.Recovery Time
Recovery from penile prosthesis implantation can take several weeks. Most patients can resume light activities within a few days to a week, but full recovery, including resuming sexual activity, typically takes 4 to 6 weeks. Patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising, but these symptoms usually resolve within a couple of weeks. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding wound care, activity restrictions, and using the prosthesis after the initial healing period.Estimated Cost
The cost of penile prosthesis implantation can vary depending on the type of prosthesis, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential adjustments or replacements of the prosthesis.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for penile prosthesis implantation includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper healing of the surgical site. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions, which may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding certain activities, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor healing and learn how to properly use the prosthesis. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
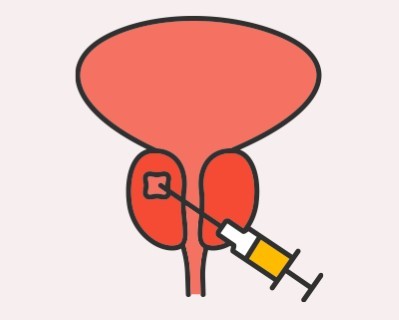
Prostate Biopsy
- Purpose: Diagnoses prostate cancer by obtaining tissue samples from the prostate.
- Procedure: A needle is inserted into the prostate to collect tissue samples.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Prostate Biopsy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the reason for the biopsy, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Prostate biopsy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the biopsy is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing a prostate biopsy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once they have recovered from any sedation.Type of Anesthesia
Prostate biopsy is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. In some cases, light sedation or general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as bleeding or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for prostate biopsy involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if sedation is used, and taking prescribed antibiotics to prevent infection. Patients should also arrange for transportation home after the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The prostate biopsy procedure typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes. During the procedure, the healthcare provider uses a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) to guide a needle into the prostate to take small tissue samples for analysis.Recovery Time
Recovery from a prostate biopsy is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, blood in the urine or semen, or minor rectal bleeding, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days to a week. It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for managing these symptoms and to complete the course of prescribed antibiotics to prevent infection.Estimated Cost
The cost of a prostate biopsy can vary depending on the healthcare provider's expertise, the method used (e.g., traditional or MRI-guided), and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and pathology analysis of the biopsy samples.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for a prostate biopsy includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or excessive bleeding. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking prescribed antibiotics, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding strenuous activities for a few days. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to discuss the biopsy results and plan any further treatment if needed. Any signs of complications, such as difficulty urinating or persistent bleeding, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Nephrectomy
- Purpose: Removes a kidney to treat kidney cancer or other kidney diseases.
- Procedure: The kidney is surgically removed through an incision in the abdomen.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Nephrectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the type of nephrectomy (partial or radical), the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Nephrectomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity of the surgery, requiring a hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing nephrectomy generally require a hospital stay of 3 to 7 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor kidney function, manage pain, and prevent complications such as bleeding or infection.Type of Anesthesia
Nephrectomy is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for nephrectomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work, imaging studies, and possibly renal function tests. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The nephrectomy procedure typically lasts between 2 to 4 hours, depending on whether it is a partial nephrectomy (removal of part of the kidney) or a radical nephrectomy (removal of the entire kidney along with surrounding tissues). The surgeon may use open surgery, laparoscopic techniques, or robotic-assisted methods, depending on the patient’s situation and the surgeon’s expertise.Recovery Time
Recovery from nephrectomy can take several weeks to months. Most patients can begin light activities within 2 to 4 weeks, but full recovery, including the return to normal activities, may take up to 6 weeks or longer. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and any actions that put strain on the abdominal area during the initial recovery period to prevent complications.Estimated Cost
The cost of nephrectomy can vary depending on the type of surgery (partial or radical), the surgical method used, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for nephrectomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients may have drainage tubes in place for a few days after surgery to remove excess fluid from the surgical site. They should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and diet. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess kidney function, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, difficulty urinating, or abnormal discharge from the incision site, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.

Circumcision
- Purpose: Removes the foreskin of the penis for medical or cultural reasons.
- Procedure: The foreskin is surgically removed.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Circumcision procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s age, underlying medical conditions, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Circumcision is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the procedure is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing circumcision generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once they have recovered from any anesthesia or sedation.Type of Anesthesia
Circumcision is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the penile area to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia or light sedation may be used, especially for young children or adults.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as bleeding or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for circumcision involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding and arranging for transportation home after the procedure if sedation or general anesthesia is used. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The circumcision procedure typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes. During the procedure, the healthcare provider removes the foreskin covering the head of the penis, either using a scalpel or surgical scissors. The incision is then closed with sutures or surgical glue.Recovery Time
Recovery from circumcision is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a day or two. Some swelling, mild pain, or bruising in the penile area is common, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days to a week. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, sexual activity, and immersion in water (e.g., baths, swimming pools) for about a week to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of circumcision can vary depending on the healthcare provider's expertise, the method used (traditional or laser), and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care or specific post-operative supplies.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for circumcision includes monitoring the surgical site for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or excessive swelling. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care, which may include applying prescribed ointments, keeping the area clean and dry, and wearing loose-fitting clothing. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure proper healing. Any signs of complications, such as fever, persistent pain, or abnormal discharge, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240721205621116577__0.webp)
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
- Purpose: Removes large kidney stones through a small incision in the back.
- Procedure: A nephroscope is used to locate and remove kidney stones.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of kidney stones, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
PCNL is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity of the surgery and the need for post-operative monitoring.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing PCNL generally require a hospital stay of 2 to 4 days, depending on the size and number of stones being treated and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, monitor kidney function, and prevent complications such as bleeding or infection.Type of Anesthesia
PCNL is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as bleeding, pain, or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for PCNL involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work, imaging studies, and possibly renal function tests. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The PCNL procedure typically lasts between 2 to 4 hours, depending on the complexity of the case. During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the patient's back to access the kidney and uses specialized instruments to break up and remove the kidney stones.Recovery Time
Recovery from PCNL can take several weeks. Most patients can begin light activities within 1 to 2 weeks, but full recovery, including the return to normal activities, may take up to 4 to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and actions that put strain on the abdominal area during the initial recovery period to prevent complications.Estimated Cost
The cost of PCNL can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the size and number of stones being treated, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for PCNL includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients may have a nephrostomy tube in place for a few days after surgery to drain urine from the kidney. They should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and diet. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess kidney function, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, difficulty urinating, or abnormal discharge from the incision site, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240721205818717884__0.webp)
Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE)
- Purpose: Retrieves sperm directly from the testicles for use in assisted reproductive technologies.
- Procedure: A small incision is made in the testicle to extract sperm.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the underlying reason for the procedure, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
TESE is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the procedure is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing TESE generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once they have recovered from any sedation or anesthesia.Type of Anesthesia
TESE is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation, which numbs the scrotal area and keeps the patient relaxed and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s preference and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or swelling.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for TESE involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding and arranging for transportation home after the procedure if sedation or general anesthesia is used. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The TESE procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 1 hour. During the procedure, the healthcare provider makes a small incision in the testicle to retrieve sperm directly from the testicular tissue, which is then analyzed and preserved for use in assisted reproductive techniques, such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).Recovery Time
Recovery from TESE is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a day or two. Some swelling, mild pain, or bruising in the scrotal area is common, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days to a week. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, sexual activity, and heavy lifting for about a week to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of TESE can vary depending on the healthcare provider's expertise, the method used, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and sperm storage if needed.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for TESE includes monitoring the surgical site for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or excessive swelling. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care, which may include applying prescribed ointments, using ice packs to reduce swelling, and wearing supportive underwear. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to discuss the results of the procedure and plan any further fertility treatments. Any signs of complications, such as fever, persistent pain, or abnormal discharge, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Cystectomy
- Purpose: Removes the bladder to treat bladder cancer or other severe bladder conditions.
- Procedure: The bladder is surgically removed, and a new way for urine to exit the body is created.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Cystectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the extent of the bladder cancer or disease, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Cystectomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to its complexity and the need for extensive post-operative monitoring and recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing cystectomy generally require a hospital stay of 7 to 10 days, depending on the extent of the surgery (partial or radical) and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor for complications, manage pain, and assist with the early stages of recovery.Type of Anesthesia
Cystectomy is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 6 to 8 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection, pain, or difficulty with the urinary diversion.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for cystectomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work, imaging studies, and possibly nutritional assessments. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The cystectomy procedure typically lasts between 4 to 6 hours, depending on whether it is a partial or radical cystectomy. During the surgery, the surgeon removes part or all of the bladder and may also create a new way for urine to exit the body, such as a urostomy or neobladder.Recovery Time
Recovery from cystectomy can take several months. Most patients can begin light activities within 4 to 6 weeks, but full recovery, including adapting to any urinary diversion, may take up to 3 months or longer. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and actions that put strain on the abdominal area during the initial recovery period to prevent complications.Estimated Cost
The cost of cystectomy can vary depending on the type of surgery (partial or radical), the surgical method used, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care, stoma care supplies, and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for cystectomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients may have drains and catheters in place for a few days after surgery to remove excess fluid and urine from the surgical site. They should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and diet. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess the function of any urinary diversion, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, difficulty urinating, or abnormal discharge from the incision site, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
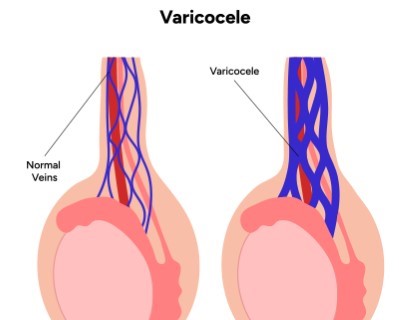
Varicocele Repair
- Purpose: Treats varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) to relieve pain and improve fertility.
- Procedure: The affected veins are surgically tied off or removed.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Varicocele Repair procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and severity of the varicocele, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Varicocele repair is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the procedure is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing varicocele repair generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Varicocele repair is usually performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the surgical technique and the patient’s condition. Local anesthesia with sedation is common for less invasive methods, while general anesthesia may be used for more complex repairs.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or swelling.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for varicocele repair involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if general anesthesia is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The varicocele repair procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 1 hour. During the procedure, the surgeon will either block or remove the affected veins using techniques such as open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or percutaneous embolization.Recovery Time
Recovery from varicocele repair is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a few days. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising in the scrotal area, but these symptoms typically resolve within a week to 10 days. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sexual activity for about 1 to 2 weeks to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of varicocele repair can vary depending on the surgical technique used, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential repeat procedures.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for varicocele repair includes monitoring the surgical site for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or excessive swelling. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care, which may include applying prescribed ointments, using ice packs to reduce swelling, and wearing supportive underwear. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure proper healing and to monitor the effectiveness of the repair. Any signs of complications, such as fever, persistent pain, or abnormal discharge, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Intravesical Therapy
Purpose:
Intravesical therapy is used to treat bladder cancer and certain other bladder conditions by delivering medication directly into the bladder. This targeted approach can be effective for managing superficial bladder cancer or preventing cancer recurrence.
Procedure:
Medication is introduced into the bladder through a catheter inserted into the urethra. The medication is retained in the bladder for a specified period to maximize its effectiveness before being drained.
Note:
The following information pertains to standard intravesical therapy procedures under typical conditions. Specifics may vary based on the type of medication used, the patient's condition, and any potential complications. Patients considering this therapy should consult with their healthcare provider to understand the full scope of the treatment.
Inpatient/Outpatient:
Intravesical therapy is usually performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing patients to return home the same day after treatment.
Hospital Stay Duration:
Patients undergoing intravesical therapy typically do not require a hospital stay. The procedure is performed in a clinical setting, and patients can usually leave shortly after the medication is administered.
Type of Anesthesia:
The procedure is generally done under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. However, general anesthesia or sedation may be used in certain cases depending on patient needs and preferences.
Travel After Procedure:
Patients are usually advised to avoid long-distance travel immediately after the procedure to monitor for any potential side effects or complications, such as bladder discomfort or infection. It is generally safe to resume normal activities within a day or two.
Pre-procedure Preparation:
Preparation for intravesical therapy includes following guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that might interfere with the treatment. Patients should ensure they have no urinary tract infections before the procedure and may need to follow specific instructions for fluid intake.
Procedure Duration:
The procedure typically lasts between 30 to 60 minutes. During this time, the medication is introduced into the bladder and allowed to remain for a prescribed duration before being removed.
Recovery Time:
Recovery from intravesical therapy is generally quick. Patients might experience mild discomfort or a frequent need to urinate immediately after the procedure, but these symptoms usually resolve within a few days. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for managing any post-procedure symptoms and attend follow-up appointments as scheduled.
Estimated Cost:
The cost of intravesical therapy can vary based on factors such as the type of medication used, the healthcare provider’s expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care or additional treatments.
Post-procedure Care:
Post-procedure care includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as increased bladder discomfort, fever, or unusual discharge. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding hydration, activity levels, and any prescribed medications. Regular follow-up visits are important to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and address any concerns. Any significant or persistent symptoms should be reported to the healthcare provider promptly.
Ureteral Stent Placement
- Purpose: Keeps the ureter open to allow urine to flow from the kidney to the bladder. This procedure is often used to treat or prevent blockages caused by kidney stones, tumors, or inflammation following surgery.
- Procedure: A flexible stent is inserted into the ureter using a cystoscope, which is guided through the urethra and bladder. The stent ensures the ureter remains open, facilitating proper urine drainage.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Ureteral Stent Placement procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the reason for the stent placement, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Ureteral stent placement is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the procedure is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing ureteral stent placement generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Ureteral stent placement is usually performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia (such as spinal anesthesia) to ensure the patient is comfortable and free of pain during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain or difficulty urinating.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for ureteral stent placement involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure if anesthesia is used. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The ureteral stent placement procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 1 hour. During the procedure, the healthcare provider inserts a thin, flexible tube (stent) into the ureter to help urine flow from the kidney to the bladder, relieving any blockages or obstructions.Recovery Time
Recovery from ureteral stent placement is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, urinary frequency, or blood in the urine, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids to help flush the urinary system and prevent infection.Estimated Cost
The cost of ureteral stent placement can vary depending on the reason for the procedure, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential stent removal.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for ureteral stent placement includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, fever, or difficulty urinating. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding strenuous activities, and scheduling follow-up appointments to monitor the stent's position and function. The stent is usually temporary and may need to be removed or replaced after a certain period, which will be determined by the healthcare provider. Any signs of complications, such as persistent pain, blood in the urine, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
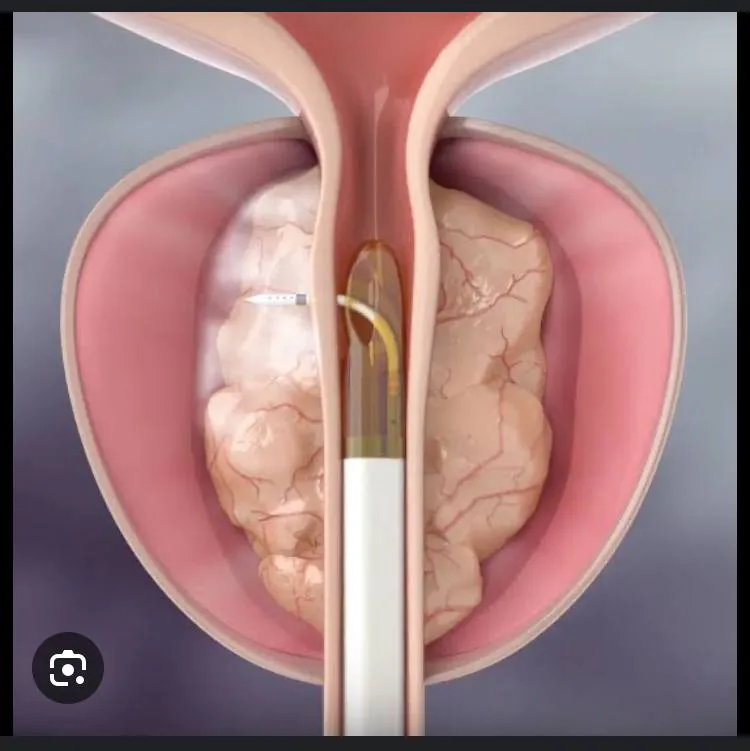
Rezum Treatment
Purpose: Treats benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by reducing the size of the prostate gland, improving urinary flow and symptoms.
Procedure:
- Rezum Water Vapor Therapy: Water vapor is delivered directly into the prostate tissue using a special device, causing the excess prostate tissue to shrink and alleviate urinary obstruction
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Rezum Treatment procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of the prostate enlargement, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Rezum treatment is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Rezum treatment generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from the anesthesia or sedation.Type of Anesthesia
Rezum treatment is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation to keep the patient comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare provider’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow time for initial recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or urinary issues.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for Rezum treatment involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if sedation or general anesthesia is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The Rezum procedure typically lasts between 10 to 20 minutes. During the procedure, the healthcare provider uses a specialized device to deliver targeted water vapor (steam) into the prostate tissue, causing the excess tissue to shrink and relieving symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).Recovery Time
Recovery from Rezum treatment is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, blood in the urine, or increased urinary frequency or urgency, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days to weeks as the prostate tissue heals and shrinks. Full symptom relief may take up to 3 months.Estimated Cost
The cost of Rezum treatment can vary depending on the healthcare provider's expertise, the complexity of the procedure, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential repeat treatments.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for Rezum treatment includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or difficulty urinating. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking prescribed medications to manage symptoms and prevent infection, staying hydrated, and avoiding strenuous activities for a few days. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and assess symptom improvement. Any signs of complications, such as persistent pain, fever, or urinary retention, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20241019184231318903__0.webp)
HoLEP (Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate)
Purpose: Treats benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by removing excess prostate tissue to relieve urinary symptoms.
Procedure:
- Holmium Laser Enucleation: A laser is used to enucleate the overgrown prostate tissue, which is then removed through the urinary tract. This minimally invasive procedure allows for precise removal of the tissue with minimal bleeding.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard HoLEP (Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of the prostate enlargement, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
HoLEP is typically performed as an inpatient procedure, though it may also be done as an outpatient procedure depending on the patient’s condition. Patients generally stay in the hospital for observation overnight.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing HoLEP usually require a hospital stay of 1 to 2 days, depending on their recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor for complications, manage pain, and ensure proper urinary function before discharge.Type of Anesthesia
HoLEP is typically performed under general or spinal anesthesia, ensuring the patient is comfortable and free of pain during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow time for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as urinary retention, bleeding, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for HoLEP involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if anesthesia is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The HoLEP procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the procedure, the surgeon uses a holmium laser to enucleate and remove the obstructive prostate tissue, which is then passed through the bladder and removed from the body.Recovery Time
Recovery from HoLEP is generally faster than traditional prostate surgeries. Most patients can resume light activities within a few days, but full recovery may take a few weeks. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, urinary urgency, or frequency, and blood in the urine, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days to weeks as the prostate heals. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sexual activity for several weeks to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of HoLEP can vary depending on the healthcare provider's expertise, the complexity of the procedure, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for HoLEP includes monitoring for any signs of complications, such as severe pain, infection, or difficulty urinating. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include taking prescribed medications, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain activities to promote healing. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and assess urinary function. Any signs of complications, such as persistent pain, fever, or difficulty urinating, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
