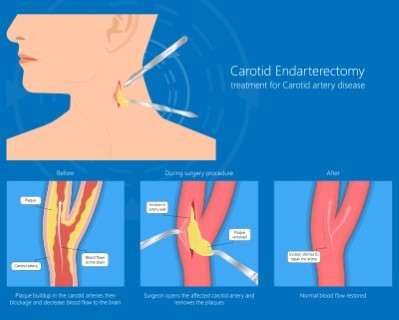
Carotid Endarterectomy
- Purpose: Removes plaque buildup from the carotid arteries to prevent stroke.
- Procedure: The artery is opened, and the plaque is surgically removed.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Carotid Endarterectomy procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of carotid artery stenosis, the presence of other vascular or heart conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the artery blockage, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Carotid Endarterectomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Due to the nature of the surgery, which involves the removal of plaque from the carotid artery to prevent stroke, patients are usually admitted to the hospital for close monitoring before, during, and after the procedure. Most patients require a hospital stay to ensure stable recovery and to monitor for any potential complications.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Carotid Endarterectomy usually stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days. The initial post-operative period involves monitoring in a specialized care unit to observe for any complications, such as stroke, bleeding, or changes in blood pressure. The length of stay may be extended if the patient has other underlying conditions or if complications arise during recovery.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, which ensures that the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the surgery. In some cases, local anesthesia with sedation may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s preference.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel for at least one to two weeks after the procedure, particularly long-distance or air travel. This allows time for initial recovery and ensures that any complications can be promptly managed. The healthcare provider will provide specific recommendations based on the patient’s recovery progress.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the surgery, patients are usually instructed to fast for several hours. A thorough pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as a carotid ultrasound or CT angiography), and evaluations by the surgical and anesthesia teams. Medication adjustments, particularly concerning blood thinners, may be necessary to minimize the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The Carotid Endarterectomy procedure typically takes 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the artery blockage and the patient’s overall condition. The surgery involves removing the plaque from the carotid artery to restore normal blood flow to the brain and reduce the risk of stroke.Recovery Time
Recovery from Carotid Endarterectomy generally takes a few weeks. Most patients can return to light activities within a week, but full recovery, including the resumption of normal activities and work, may take several weeks. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding activity levels, medication management, and any necessary lifestyle changes post-surgery.Estimated Cost
The cost of Carotid Endarterectomy can vary depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is essential for a successful recovery after Carotid Endarterectomy. Patients will need to monitor their incision site for signs of infection or bleeding, manage pain with prescribed medications, and attend follow-up appointments to monitor the success of the procedure. Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider are crucial to ensure the carotid artery remains clear and to manage any ongoing risk factors for stroke. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, to improve overall vascular health and prevent future blockages.