Cardiovascular Surgery Treatments
_20240719134043823044__0.webp)
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
- Purpose: Improves blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked coronary arteries.
- Procedure: A blood vessel from another part of the body is grafted to bypass the blocked artery.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of coronary artery disease, the presence of other health conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the bypass procedure, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the surgery and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
CABG is a major surgical procedure and is typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Patients are admitted to the hospital and remain under close observation before, during, and after the surgery. This extended hospital stay is necessary to monitor heart function, manage pain, and ensure a stable recovery. Most patients require several days in the hospital following the surgery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing CABG usually stay in the hospital for 5 to 7 days. This period allows for intensive monitoring, especially in the first 24 to 48 hours, typically in a specialized cardiac care unit. During this time, the healthcare team monitors for complications such as arrhythmias, infections, or issues with the grafts. The length of stay may be extended if complications arise or if the patient has other underlying conditions that require additional care.Type of Anesthesia
CABG is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is fully unconscious during the procedure. General anesthesia ensures the patient is comfortable and still, which is crucial for the precision required in open-heart surgery.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel, especially air travel, for at least 4 to 6 weeks after CABG surgery. This period allows time for recovery, healing of the sternum (breastbone), and stabilization of heart function. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s specific recommendations regarding travel and activity levels post-surgery.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the surgery, patients are typically instructed to fast for several hours. A comprehensive pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as an echocardiogram or coronary angiography), and evaluations by anesthesia and cardiac teams. Patients may need to adjust or stop certain medications, particularly blood thinners, as directed by their healthcare provider to reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The CABG procedure typically takes 3 to 6 hours, depending on the number of arteries being bypassed and the complexity of the case. The surgery involves using a graft (usually taken from the patient’s leg, arm, or chest) to bypass the blocked coronary arteries, improving blood flow to the heart.Recovery Time
Recovery from CABG is gradual and can take several weeks to a few months. Most patients are advised to engage in light activities, such as walking, soon after discharge, but full recovery, including a return to work and more strenuous activities, may take up to 12 weeks or longer. Patients will participate in a cardiac rehabilitation program to help regain strength and learn how to manage their heart health post-surgery.Estimated Cost
The cost of CABG can vary widely depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is critical for successful recovery after CABG. Patients need to monitor their incision sites for signs of infection, manage pain with prescribed medications, and adhere to a strict rehabilitation plan. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor heart function, check the status of the grafts, and manage any long-term medications. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, to support heart health and prevent further cardiac issues.
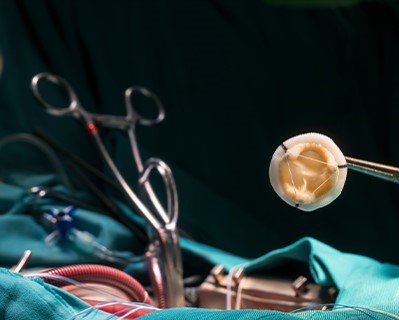
Heart Valve Replacement
- Purpose: Replaces damaged or diseased heart valves to restore normal blood flow.
- Procedure: The damaged valve is removed and replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Heart Valve Replacement procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of valve disease, the presence of other heart or systemic conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the type of valve replacement (mechanical or biological), and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Heart Valve Replacement is a major surgical procedure and is typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Patients are admitted to the hospital and remain under close observation before, during, and after the surgery. Due to the complexity of the procedure, most patients require several days in the hospital following surgery for intensive monitoring and recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Heart Valve Replacement usually stay in the hospital for 5 to 7 days. The first 24 to 48 hours are often spent in a specialized cardiac care unit (CCU) for close monitoring of heart function, blood pressure, and the new valve. The total length of stay may vary based on the patient’s overall condition, the type of valve used, and any post-operative complications that may arise.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient will be fully unconscious during the surgery. General anesthesia ensures the patient remains still and comfortable, which is essential for the precision required in heart surgery.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel, particularly air travel, for at least 4 to 6 weeks after Heart Valve Replacement surgery. This period allows for adequate recovery and healing, especially of the sternum (breastbone) if it was opened during surgery. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s specific recommendations regarding travel and physical activity after surgery.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before surgery, patients are typically instructed to fast for several hours. A thorough pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as echocardiograms or CT scans), and evaluations by anesthesia and surgical teams. Medication adjustments, particularly concerning blood thinners, may be necessary to minimize the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The Heart Valve Replacement procedure usually takes 3 to 5 hours, depending on the complexity of the case and whether other procedures, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), are performed simultaneously. The surgery involves removing the damaged valve and replacing it with either a mechanical or biological prosthetic valve.Recovery Time
Recovery from Heart Valve Replacement surgery can take several weeks to a few months. Patients are encouraged to engage in light activities, such as walking, soon after discharge, but full recovery, including returning to work and more strenuous activities, may take up to 12 weeks or longer. Participation in a cardiac rehabilitation program is often recommended to help regain strength and learn how to manage heart health after surgery.Estimated Cost
The cost of Heart Valve Replacement surgery can vary widely depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition and valve choice. Mechanical valves often require lifelong anticoagulation therapy, which may affect long-term costs. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is essential for successful recovery after Heart Valve Replacement. Patients need to monitor their incision sites for signs of infection, manage pain with prescribed medications, and follow a structured rehabilitation plan. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the function of the new valve, adjust medications, and ensure overall heart health. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and medication management, to support long-term heart health and prevent future complications.

Aneurysm Repair
- Purpose: Repairs aneurysms to prevent rupture and bleeding.
- Procedure: The weakened section of the blood vessel is replaced with a synthetic graft.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective surgical Aneurysm Repair procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and location of the aneurysm, the presence of other health conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the aneurysm, and the type of surgical approach used (open or endovascular) can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Surgical Aneurysm Repair is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity and seriousness of the surgery. Patients are admitted to the hospital and are closely monitored before, during, and after the surgery. The extent of the hospital stay depends on the type of repair (open surgery vs. endovascular) and the patient’s overall condition.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing open Aneurysm Repair usually stay in the hospital for 5 to 10 days, with the first few days spent in an intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring. If an endovascular approach is used, the hospital stay might be shorter, typically 2 to 5 days, depending on the patient’s recovery and the complexity of the procedure. The length of stay can be longer if complications arise or if the patient has other underlying health issues that require additional care.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious during the surgery. This is necessary to keep the patient comfortable and still, allowing the surgical team to perform the complex and delicate repairs required to treat the aneurysm.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel, particularly long-distance or air travel, for at least 4 to 6 weeks after surgical Aneurysm Repair. This period allows for adequate recovery and healing, particularly if the patient underwent open surgery, which involves a more extended recovery time. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s specific recommendations regarding travel and physical activity after surgery.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before surgery, patients are usually instructed to fast for several hours. A comprehensive pre-operative assessment, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as CT scans or MRIs), and evaluations by anesthesia and surgical teams, is conducted to plan the surgery. Patients may need to adjust or stop taking certain medications, particularly blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The duration of surgical Aneurysm Repair can vary significantly, typically ranging from 3 to 6 hours depending on the location of the aneurysm, the complexity of the case, and whether open or endovascular techniques are used. Open surgery generally takes longer than endovascular repair.Recovery Time
Recovery from surgical Aneurysm Repair can take several weeks to several months, depending on the type of surgery performed and the patient’s overall health. Patients who undergo open surgery may require a longer recovery period, with light activities resumed within a few weeks and more strenuous activities after several months. Patients who undergo endovascular repair typically have a shorter recovery time but still need to follow strict guidelines for activity and follow-up care.Estimated Cost
The cost of Aneurysm Repair surgery can vary widely depending on the hospital, geographic location, the type of repair (open vs. endovascular), and the specifics of the patient’s condition. Open surgery generally involves a longer hospital stay and recovery period, which can increase costs. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is crucial for a successful recovery after Aneurysm Repair. Patients will need to monitor their incision sites for signs of infection, manage pain with prescribed medications, and adhere to a structured rehabilitation plan. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the repair, check for any signs of recurrence or complications, and manage any long-term medications. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, to reduce the risk of future aneurysms and improve overall vascular health.
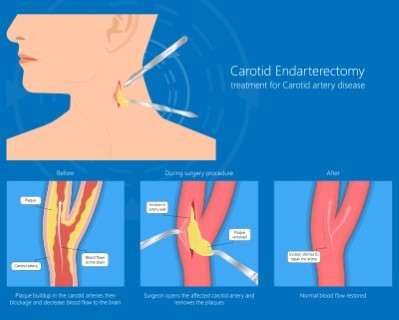
Carotid Endarterectomy
- Purpose: Removes plaque buildup from the carotid arteries to prevent stroke.
- Procedure: The artery is opened, and the plaque is surgically removed.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Carotid Endarterectomy procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of carotid artery stenosis, the presence of other vascular or heart conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the artery blockage, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Carotid Endarterectomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Due to the nature of the surgery, which involves the removal of plaque from the carotid artery to prevent stroke, patients are usually admitted to the hospital for close monitoring before, during, and after the procedure. Most patients require a hospital stay to ensure stable recovery and to monitor for any potential complications.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Carotid Endarterectomy usually stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days. The initial post-operative period involves monitoring in a specialized care unit to observe for any complications, such as stroke, bleeding, or changes in blood pressure. The length of stay may be extended if the patient has other underlying conditions or if complications arise during recovery.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, which ensures that the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the surgery. In some cases, local anesthesia with sedation may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s preference.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel for at least one to two weeks after the procedure, particularly long-distance or air travel. This allows time for initial recovery and ensures that any complications can be promptly managed. The healthcare provider will provide specific recommendations based on the patient’s recovery progress.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the surgery, patients are usually instructed to fast for several hours. A thorough pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as a carotid ultrasound or CT angiography), and evaluations by the surgical and anesthesia teams. Medication adjustments, particularly concerning blood thinners, may be necessary to minimize the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The Carotid Endarterectomy procedure typically takes 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the artery blockage and the patient’s overall condition. The surgery involves removing the plaque from the carotid artery to restore normal blood flow to the brain and reduce the risk of stroke.Recovery Time
Recovery from Carotid Endarterectomy generally takes a few weeks. Most patients can return to light activities within a week, but full recovery, including the resumption of normal activities and work, may take several weeks. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding activity levels, medication management, and any necessary lifestyle changes post-surgery.Estimated Cost
The cost of Carotid Endarterectomy can vary depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is essential for a successful recovery after Carotid Endarterectomy. Patients will need to monitor their incision site for signs of infection or bleeding, manage pain with prescribed medications, and attend follow-up appointments to monitor the success of the procedure. Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider are crucial to ensure the carotid artery remains clear and to manage any ongoing risk factors for stroke. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, to improve overall vascular health and prevent future blockages.
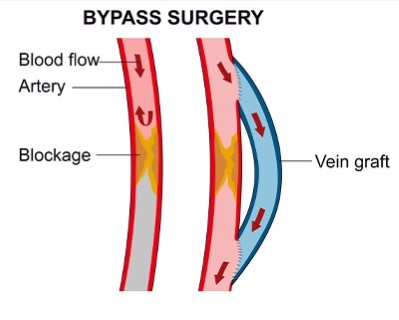
Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery
- Purpose: Bypasses blocked peripheral arteries to restore blood flow to the limbs.
- Procedure: A graft is used to bypass the blocked artery.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of peripheral artery disease, the presence of other vascular or systemic conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the bypass, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery is typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Given the nature of the surgery, which involves rerouting blood flow around a blocked artery in the leg or arm, patients are admitted to the hospital for close monitoring before, during, and after the procedure. Most patients require a hospital stay to ensure proper recovery and to monitor for any potential complications.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery usually stay in the hospital for 3 to 7 days. The initial post-operative period involves monitoring in a specialized care unit to observe for any complications, such as bleeding, infection, or issues with the graft used for the bypass. The length of stay may be extended if the patient has other underlying conditions or if complications arise during recovery.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the surgery. In some cases, regional anesthesia may be used, depending on the location of the bypass and the patient’s overall condition.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel for at least two to four weeks after the procedure, particularly long-distance or air travel. This allows time for initial recovery, including wound healing and stabilization of blood flow in the affected limb. The healthcare provider will provide specific recommendations based on the patient’s recovery progress.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the surgery, patients are typically instructed to fast for several hours. A thorough pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as Doppler ultrasound or angiography), and evaluations by the surgical and anesthesia teams. Medication adjustments, particularly concerning blood thinners, may be necessary to minimize the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery procedure typically takes 3 to 6 hours, depending on the location and complexity of the bypass and the patient’s overall condition. The surgery involves using a graft (either a vein from the patient’s body or a synthetic material) to bypass the blocked artery and restore blood flow to the affected limb.Recovery Time
Recovery from Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery generally takes several weeks to a few months. Most patients can return to light activities within a few weeks, but full recovery, including the resumption of normal activities and work, may take longer. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding activity levels, wound care, and any necessary lifestyle changes to support recovery and long-term vascular health.Estimated Cost
The cost of Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery can vary depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is crucial for a successful recovery after Peripheral Artery Bypass Surgery. Patients need to monitor the incision sites for signs of infection, manage pain with prescribed medications, and attend follow-up appointments to assess the success of the surgery and the patency of the bypass graft. Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider are essential to monitor vascular health and prevent future blockages. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, to improve overall vascular health and reduce the risk of future arterial disease.
_20240719134335164050__0.webp)
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
- Purpose: Treats aortic aneurysms using a minimally invasive approach.
- Procedure: A stent graft is placed inside the aorta to reinforce the aneurysm.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and location of the aneurysm, the presence of other vascular or systemic conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the aneurysm, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) is typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Patients are admitted to the hospital for close monitoring before, during, and after the procedure to ensure the aneurysm is successfully treated and to monitor for any potential complications. While EVAR is less invasive than open surgery, most patients require a short hospital stay for observation.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing EVAR usually stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days. This period allows for close monitoring to ensure that the endograft (the device used to reinforce the artery) is properly placed and that there are no immediate complications, such as bleeding, infection, or issues with the stent graft. The length of stay may be extended if complications arise or if the patient has other underlying conditions requiring additional care.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under regional anesthesia with sedation, or in some cases, under general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and the complexity of the aneurysm. Regional anesthesia allows the patient to remain awake but relaxed, while the surgical team accesses the aneurysm through small incisions in the groin.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel for at least one to two weeks after the procedure, particularly long-distance or air travel. This allows time for initial recovery, including ensuring the stent graft is functioning correctly and that there are no complications. The healthcare provider will provide specific recommendations based on the patient’s recovery progress.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients are usually instructed to fast for several hours. A comprehensive pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as CT angiography), and evaluations by the surgical and anesthesia teams. Medication adjustments, particularly concerning blood thinners, may be necessary to minimize the risk of bleeding during the procedure.Procedure Duration
The EVAR procedure typically takes 2 to 4 hours, depending on the complexity of the aneurysm and the patient’s overall condition. The procedure involves inserting a stent graft through the femoral arteries in the groin and guiding it to the site of the aneurysm, where it is deployed to reinforce the weakened section of the artery.Recovery Time
Recovery from EVAR is generally quicker than recovery from open aneurysm repair. Most patients can return to light activities within a week, though full recovery, including a return to more strenuous activities, may take a few weeks. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding activity levels, wound care, and any necessary follow-up imaging to monitor the success of the procedure.Estimated Cost
The cost of EVAR can vary depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is crucial for a successful recovery after EVAR. Patients need to monitor the incision sites for signs of infection, manage pain with prescribed medications, and attend regular follow-up appointments to assess the success of the procedure and to monitor the aneurysm repair. Regular imaging studies, such as CT scans or ultrasounds, are often required to ensure the stent graft remains in place and the aneurysm is not enlarging. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, to improve overall vascular health and reduce the risk of future aneurysms.
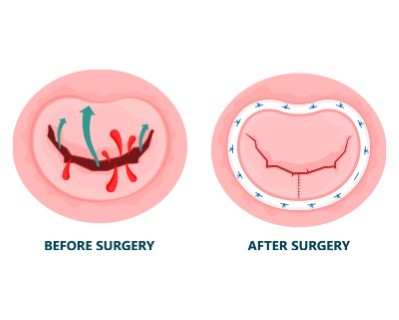
Mitral Valve Repair
- Purpose: Repairs the mitral valve to improve blood flow and prevent regurgitation.
- Procedure: The mitral valve is surgically repaired using various techniques.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Mitral Valve Repair procedures under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of mitral valve disease, the presence of other heart or systemic conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the surgery. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the valve repair, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Mitral Valve Repair is a major surgical procedure typically performed as an inpatient procedure. Patients are admitted to the hospital and remain under close observation before, during, and after the surgery. Most patients will require a hospital stay to monitor heart function and ensure proper recovery, especially given the complexity of the surgery and the potential for complications.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Mitral Valve Repair usually stay in the hospital for 5 to 7 days. The initial post-operative period involves close monitoring in a specialized cardiac care unit (CCU) for at least 24 to 48 hours. During this time, the healthcare team monitors for complications such as arrhythmias, infections, or issues with the repaired valve. The length of stay may be extended if the patient has other underlying conditions or if complications arise during recovery.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient will be fully unconscious during the surgery. General anesthesia is necessary to keep the patient comfortable and still, allowing the surgical team to perform the intricate repairs needed to correct the mitral valve’s function.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid travel, particularly long-distance or air travel, for at least 4 to 6 weeks after Mitral Valve Repair surgery. This period allows time for initial recovery and healing, especially of the sternum (breastbone) if it was opened during surgery. The healthcare provider will provide specific recommendations regarding travel and activity levels based on the patient’s recovery progress.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the surgery, patients are typically instructed to fast for several hours. A comprehensive pre-operative assessment is conducted, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as echocardiograms or CT scans), and evaluations by anesthesia and cardiac teams. Medication adjustments, particularly concerning blood thinners, may be necessary to minimize the risk of bleeding during surgery.Procedure Duration
The Mitral Valve Repair procedure usually takes 3 to 5 hours, depending on the complexity of the repair and whether other procedures, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), are performed simultaneously. The surgery involves repairing the mitral valve’s leaflets, chords, or annulus to restore normal valve function.Recovery Time
Recovery from Mitral Valve Repair surgery can take several weeks to a few months. Most patients are encouraged to engage in light activities, such as walking, soon after discharge, but full recovery, including a return to work and more strenuous activities, may take up to 12 weeks or longer. Participation in a cardiac rehabilitation program is often recommended to help regain strength and learn how to manage heart health after surgery.Estimated Cost
The cost of Mitral Valve Repair surgery can vary widely depending on the hospital, geographic location, and the specifics of the patient’s condition and the complexity of the repair. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or hospital directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care is critical for a successful recovery after Mitral Valve Repair. Patients need to monitor their incision sites for signs of infection, manage pain with prescribed medications, and adhere to a strict rehabilitation plan. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the function of the repaired valve, adjust medications, and ensure overall heart health. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and medication management, to support long-term heart health and prevent future complications.
_20240719153757410714__0.webp)
Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Laser Therapy - EVLT)
- Purpose: Treats varicose veins to improve appearance and alleviate symptoms.
- Procedure: A laser fiber is inserted into the vein to heat and close it.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Varicose Vein Treatment using Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT) under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of varicose veins, the presence of other vascular conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the complexity of the vein issues, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT) for varicose veins is typically performed as an outpatient procedure. This minimally invasive treatment allows most patients to return home the same day, with minimal disruption to their daily activities. However, in cases where the procedure is more complex or if multiple veins are treated, a short observation period may be required.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing EVLT typically do not require an overnight hospital stay. The procedure is usually completed within a few hours, and patients are monitored briefly afterward to ensure there are no immediate complications. Most patients can go home the same day, but those with more extensive treatments may need to stay for a few hours of observation.Type of Anesthesia
EVLT is performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area around the vein being treated. This ensures that the patient is comfortable throughout the procedure. In some cases, mild sedation may also be provided to help the patient relax, though general anesthesia is not typically required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel, particularly air travel, for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure. This allows time for initial recovery and to ensure there are no complications such as blood clots. Light activities are usually encouraged, but patients should follow specific recommendations from their healthcare provider regarding travel and activity levels.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, particularly blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding. The healthcare provider will provide specific instructions, including fasting requirements if any, and patients may undergo a pre-procedure ultrasound to map the veins for treatment.Procedure Duration
The EVLT procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour per leg, depending on the number and size of the veins being treated. The procedure involves using laser energy to close off the affected veins, which are then gradually absorbed by the body.Recovery Time
Recovery from EVLT is generally quick, with most patients returning to their normal activities within a day or two. Patients are usually encouraged to walk and stay active to promote circulation, but they should avoid strenuous exercise for a few days. Full recovery, including the resolution of any swelling or bruising, typically occurs within a few weeks.Estimated Cost
The cost of EVLT can vary depending on the clinic, geographic location, and the extent of the treatment needed. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or treatment center directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for EVLT includes wearing compression stockings for a few days to a few weeks, as recommended by the healthcare provider, to support healing and reduce swelling. Patients should monitor the treated area for signs of complications, such as redness, pain, or swelling, and attend follow-up appointments to assess the success of the treatment. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent future varicose veins, such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
_20240719134443767135__0.webp)
Sclerotherapy (for Varicose Veins)
- Purpose: Treats varicose and spider veins by causing them to collapse and fade.
- Procedure: A sclerosing solution is injected into the veins.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Sclerotherapy for the treatment of varicose veins under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and extent of the varicose veins, the presence of other vascular conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the number of veins treated, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Sclerotherapy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure. It is a minimally invasive treatment that allows most patients to return home the same day. This procedure is often done in a doctor’s office or a specialized clinic, with no need for hospital admission.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Sclerotherapy typically do not require any hospital stay. The procedure is usually completed in about 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the number and size of veins being treated. After the procedure, patients are observed for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications, and they can usually go home the same day.Type of Anesthesia
Sclerotherapy is generally performed without the need for anesthesia. The procedure involves injecting a sclerosing solution directly into the affected veins, which causes them to close off and eventually be reabsorbed by the body. While some patients may experience mild discomfort during the injections, anesthesia is not typically required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are usually able to travel shortly after the procedure, although it is advised to avoid long periods of immobility, particularly long-distance travel, for the first 24 to 48 hours. Light walking is encouraged to promote circulation, but patients should follow specific recommendations from their healthcare provider regarding travel and activity levels.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, particularly blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding or bruising. Patients should also avoid applying lotion or oils to their legs on the day of the procedure. The healthcare provider will provide specific pre-procedure instructions tailored to the patient’s needs.Procedure Duration
The Sclerotherapy procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the extent of the veins being treated. Multiple sessions may be needed to achieve optimal results, especially for larger or more numerous varicose veins.Recovery Time
Recovery from Sclerotherapy is generally quick, with most patients able to return to normal activities immediately after the procedure. However, it is recommended to avoid strenuous exercise for a few days and to wear compression stockings as advised by the healthcare provider to support healing and improve results. Full results from the treatment may take several weeks to become apparent as the treated veins gradually fade.Estimated Cost
The cost of Sclerotherapy can vary depending on the clinic, geographic location, and the extent of the treatment needed. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or treatment center directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for Sclerotherapy includes wearing compression stockings for a few days to a few weeks, as recommended by the healthcare provider, to help compress the veins and promote healing. Patients should monitor the treated area for signs of complications, such as redness, pain, or swelling, and attend follow-up appointments to assess the success of the treatment. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent the recurrence of varicose veins, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
_20240719134510364830__0.webp)
Phlebectomy (for Varicose Veins)
- Purpose: Removes varicose veins through small incisions.
- Procedure: Tiny incisions are made along the vein, and the vein is removed with a special hook.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Phlebectomy for the treatment of varicose veins under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and extent of the varicose veins, the presence of other vascular conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the number of veins treated, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Phlebectomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure. This minimally invasive treatment allows most patients to return home the same day. It is often done in a doctor’s office or a specialized clinic, with no need for hospital admission, allowing for a quick return to normal activities.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Phlebectomy usually do not require an overnight hospital stay. The procedure typically takes about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the number and size of the veins being removed. After the procedure, patients are monitored for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications, and they are usually discharged the same day.Type of Anesthesia
Phlebectomy is generally performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area around the veins being treated. This ensures that the patient is comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, mild sedation may be provided to help the patient relax, but general anesthesia is not typically required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are usually able to travel shortly after the procedure, although it is advised to avoid long periods of immobility, particularly long-distance travel, for the first 24 to 48 hours. Light walking is encouraged to promote circulation, but patients should follow specific recommendations from their healthcare provider regarding travel and activity levels.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, particularly blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding or bruising. Patients should also avoid applying lotion or oils to their legs on the day of the procedure. The healthcare provider will provide specific pre-procedure instructions tailored to the patient’s needs.Procedure Duration
The Phlebectomy procedure typically takes about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the extent of the veins being removed. Multiple sessions may be required if a large number of veins need to be treated.Recovery Time
Recovery from Phlebectomy is generally quick, with most patients able to return to normal activities within a few days. It is recommended to avoid strenuous exercise for at least one week and to wear compression stockings as advised by the healthcare provider to support healing and improve results. Bruising and swelling are common and should subside within a few weeks.Estimated Cost
The cost of Phlebectomy can vary depending on the clinic, geographic location, and the extent of the treatment needed. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or treatment center directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for Phlebectomy includes wearing compression stockings for a few days to a few weeks, as recommended by the healthcare provider, to help compress the veins and promote healing. Patients should monitor the treated area for signs of complications, such as redness, pain, or swelling, and attend follow-up appointments to assess the success of the treatment. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent the recurrence of varicose veins, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
-(for-varicose-veins)_20240719134807209789__0.webp)
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) (for Varicose Veins)
- Purpose: Treats varicose veins by using radiofrequency energy to heat and close the veins.
- Procedure: A catheter is inserted into the vein, and radiofrequency energy is used to close it.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for the treatment of varicose veins under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and extent of the varicose veins, the presence of other vascular conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the number of veins treated, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for varicose veins is typically performed as an outpatient procedure. This minimally invasive treatment allows most patients to return home the same day, with minimal disruption to their daily activities. It is often done in a doctor’s office or a specialized clinic, with no need for hospital admission.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing RFA typically do not require an overnight hospital stay. The procedure usually takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour per leg, depending on the number and size of veins being treated. After the procedure, patients are monitored for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications, and they are usually discharged the same day.Type of Anesthesia
RFA is performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area around the vein being treated. This ensures that the patient is comfortable throughout the procedure. In some cases, mild sedation may be provided to help the patient relax, though general anesthesia is not typically required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally able to travel shortly after the procedure, although it is advised to avoid long periods of immobility, particularly long-distance travel, for the first 24 to 48 hours. Light walking is encouraged to promote circulation, but patients should follow specific recommendations from their healthcare provider regarding travel and activity levels.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, particularly blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding or bruising. Patients should also avoid applying lotion or oils to their legs on the day of the procedure. The healthcare provider will provide specific pre-procedure instructions tailored to the patient’s needs.Procedure Duration
The RFA procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the extent of the veins being treated. The procedure involves using radiofrequency energy to heat and close off the affected veins, which are then gradually absorbed by the body.Recovery Time
Recovery from RFA is generally quick, with most patients able to return to their normal activities within a day or two. Patients are usually encouraged to walk and stay active to promote circulation, but they should avoid strenuous exercise for a few days. Full recovery, including the resolution of any swelling or bruising, typically occurs within a few weeks.Estimated Cost
The cost of RFA can vary depending on the clinic, geographic location, and the extent of the treatment needed. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or treatment center directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for RFA includes wearing compression stockings for a few days to a few weeks, as recommended by the healthcare provider, to help compress the veins and promote healing. Patients should monitor the treated area for signs of complications, such as redness, pain, or swelling, and attend follow-up appointments to assess the success of the treatment. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent the recurrence of varicose veins, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
_20240719134825462451__0.webp)
Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy (for Varicose Veins)
- Purpose: Treats varicose veins using a foam sclerosant to close the veins.
- Procedure: A foam sclerosant is injected into the veins under ultrasound guidance.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to elective Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy for the treatment of varicose veins under standard conditions. However, specifics may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the size and extent of the varicose veins, the presence of other vascular conditions, or any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. The patient’s overall health, the number of veins treated, and the need for additional interventions can also influence the procedure and recovery process.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure. This minimally invasive treatment allows most patients to return home the same day. The procedure is often conducted in a doctor’s office or specialized clinic, with no need for hospital admission, making it convenient for patients with busy schedules.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy usually do not require a hospital stay. The procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the number and size of veins being treated. After the procedure, patients are monitored briefly to ensure there are no immediate complications, and they are generally discharged the same day.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is usually performed without the need for anesthesia, as it involves injecting a foam sclerosant directly into the affected veins. The foam causes the veins to collapse and eventually be absorbed by the body. While the injections may cause some mild discomfort, anesthesia is not typically required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are usually able to travel shortly after the procedure, although it is advised to avoid long periods of immobility, particularly long-distance travel, for the first 24 to 48 hours. Light walking is encouraged to promote circulation, but patients should follow specific recommendations from their healthcare provider regarding travel and activity levels.Pre-procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, particularly blood thinners, to reduce the risk of bleeding or bruising. Patients should also avoid applying lotion or oils to their legs on the day of the procedure. The healthcare provider will provide specific pre-procedure instructions tailored to the patient’s needs.Procedure Duration
The Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the extent of the veins being treated. Multiple sessions may be required for larger or more extensive varicose veins to achieve optimal results.Recovery Time
Recovery from Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy is generally quick, with most patients able to return to their normal activities within a day. Patients are typically encouraged to walk and stay active to promote circulation but should avoid strenuous exercise for a few days. Full recovery, including the resolution of any swelling or bruising, typically occurs within a few weeks.Estimated Cost
The cost of Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy can vary depending on the clinic, geographic location, and the extent of the treatment needed. For accurate cost information, patients should contact their healthcare provider or treatment center directly.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for Endovenous Foam Sclerotherapy includes wearing compression stockings for a few days to a few weeks, as recommended by the healthcare provider, to help compress the veins and promote healing. Patients should monitor the treated area for signs of complications, such as redness, pain, or swelling, and attend follow-up appointments to assess the success of the treatment. Patients will also receive guidance on lifestyle changes to prevent the recurrence of varicose veins, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
