Neurosurgery Treatments
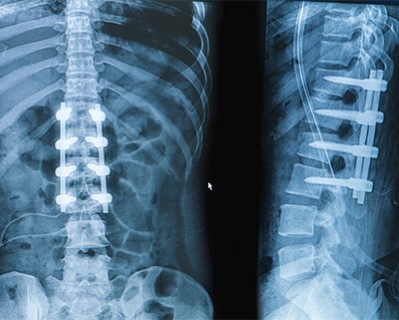
Spinal Fusion
- Purpose: To treat conditions like degenerative disc disease, scoliosis, and spinal instability by fusing two or more vertebrae.
- Procedure: Bone grafts and metal implants are used to join the vertebrae, promoting bone growth to achieve fusion.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Spinal Fusion procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the extent of the spinal condition, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Spinal fusion is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity of the surgery. Most patients will require a hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing spinal fusion generally require a hospital stay of 3 to 5 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, monitor for complications, and assist with early mobility.Type of Anesthesia
Spinal fusion is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for spinal fusion involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging and blood work. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The spinal fusion procedure typically lasts between 3 to 6 hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery and the number of vertebrae being fused. The surgeon will remove damaged discs and use bone grafts or implants to fuse the affected vertebrae, stabilizing the spine and reducing pain.Recovery Time
Recovery from spinal fusion can take several months. Most patients can begin light activities within 4 to 6 weeks, but full recovery, including bone healing, may take 6 to 12 months. Patients will need to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and twisting motions during the recovery period. Physical therapy is often recommended to help restore strength and mobility.Estimated Cost
The cost of spinal fusion can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, the type of implants or grafts used, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and rehabilitation.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for spinal fusion includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Physical therapy is typically a key component of recovery, focusing on strengthening the muscles supporting the spine. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Microdiscectomy
- Purpose: To relieve pressure on spinal nerves caused by a herniated disc.
- Procedure: The damaged portion of the disc is removed through a small incision using a microscope.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Microdiscectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and severity of the disc herniation, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Microdiscectomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing microdiscectomy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Microdiscectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as swelling, pain, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for microdiscectomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The microdiscectomy procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the surgery, the surgeon makes a small incision in the back and removes the portion of the herniated disc that is pressing on the spinal nerve, relieving pain and improving mobility.Recovery Time
Recovery from microdiscectomy is generally quicker than other spinal surgeries. Most patients can begin light activities within a few days to a week, but it is important to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or twisting for several weeks. Full recovery, including the resumption of normal activities, typically takes 4 to 6 weeks, although some patients may require longer. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the back and prevent future issues.Estimated Cost
The cost of microdiscectomy can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and physical therapy.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for microdiscectomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
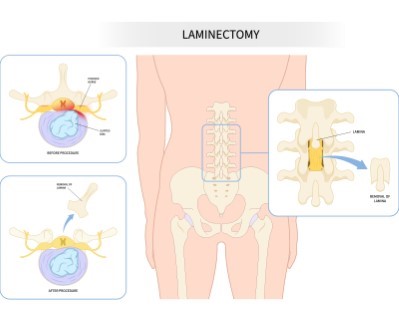
Laminectomy
- Purpose: To relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves caused by spinal stenosis or tumors.
- Procedure: The lamina (part of the vertebra) is removed to create more space for the spinal cord and nerves.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Laminectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and severity of spinal compression, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Laminectomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity of the surgery. Most patients will require a hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing laminectomy generally require a hospital stay of 1 to 3 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, monitor for complications, and assist with early mobility.Type of Anesthesia
Laminectomy is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 2 to 4 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for laminectomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging and blood work. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The laminectomy procedure typically lasts between 2 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery. During the procedure, the surgeon removes a portion of the vertebral bone called the lamina to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, often due to conditions like spinal stenosis or herniated discs.Recovery Time
Recovery from laminectomy can take several weeks. Most patients can begin light activities within 1 to 2 weeks, but full recovery, including the resumption of normal activities, typically takes 6 to 8 weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and twisting motions during the recovery period. Physical therapy is often recommended to help restore strength and mobility.Estimated Cost
The cost of laminectomy can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and rehabilitation.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for laminectomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240719143158604594__0.webp)
Vertebroplasty (Kyphoplasty)
- Purpose: To treat vertebral compression fractures, often due to osteoporosis.
- Procedure: Bone cement is injected into the fractured vertebra (vertebroplasty) or a balloon is first inflated to restore height before cement injection (kyphoplasty).
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Vertebroplasty (Kyphoplasty) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the vertebral compression fractures, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are typically performed as outpatient procedures, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
These procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation to ensure the patient is comfortable. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery if general anesthesia is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the procedure, the surgeon uses imaging guidance to insert a needle into the fractured vertebra and injects bone cement to stabilize the fracture. In kyphoplasty, a balloon is first inserted and inflated to create space and restore vertebral height before the cement is injected.Recovery Time
Recovery from vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is generally quick. Most patients experience significant pain relief within a few days and can return to light activities within a week. Full recovery, including resuming normal activities, usually occurs within 2 to 4 weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting during the initial recovery period to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and rehabilitation.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper healing of the vertebrae. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for activity restrictions and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Foraminotomy
- Purpose: To relieve pressure on nerves compressed by bone spurs or disc material.
- Procedure: Part of the bone around the neural foramen is removed to enlarge the space where nerves exit the spinal canal.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Foraminotomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and severity of the nerve compression, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Foraminotomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing foraminotomy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Foraminotomy is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, local anesthesia with sedation may be used, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s recommendation.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for foraminotomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The foraminotomy procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the surgery, the surgeon removes bone or tissue from the foramina (the openings where nerves exit the spinal column) to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves, thereby reducing pain and improving mobility.Recovery Time
Recovery from foraminotomy is generally quick compared to more extensive spinal surgeries. Most patients can return to light activities within a week, but full recovery, including resuming normal activities, typically takes 4 to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and twisting motions during the recovery period. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the back and improve flexibility.Estimated Cost
The cost of foraminotomy can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and rehabilitation.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for foraminotomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
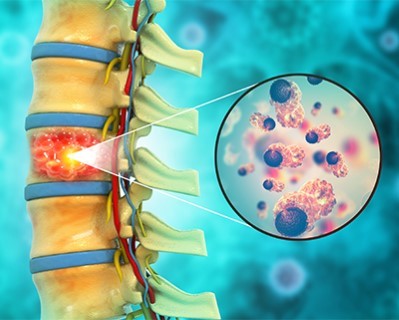
Spinal Tumor Resection
- Purpose: To remove tumors from the spinal cord or vertebrae.
- Procedure: The tumor is surgically removed, often followed by reconstruction of the spine if necessary.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Spinal Tumor Resection procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and type of the spinal tumor, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Spinal tumor resection is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity and potential risks involved. Most patients will require a hospital stay for post-operative monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing spinal tumor resection generally require a hospital stay of 3 to 7 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, monitor for complications, and assist with early mobility.Type of Anesthesia
Spinal tumor resection is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or neurological issues.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for spinal tumor resection involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging and blood work. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The spinal tumor resection procedure typically lasts between 4 to 8 hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery and the location of the tumor. The surgeon carefully removes the tumor while minimizing damage to the surrounding spinal cord and nerves.Recovery Time
Recovery from spinal tumor resection can be extensive, often taking several weeks to months. Most patients can begin light activities within 4 to 6 weeks, but full recovery, including regaining strength and mobility, may take several months. Physical therapy is often recommended to aid in recovery and improve functional outcomes.Estimated Cost
The cost of spinal tumor resection can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and rehabilitation.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for spinal tumor resection includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess neurological function, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Scoliosis Surgery
- Purpose: To correct severe spinal curvature and prevent progression.
- Procedure: Spinal fusion is often used, with metal rods and screws to straighten and stabilize the spine.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Scoliosis Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the spinal curvature, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Scoliosis surgery is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity of the surgery. Most patients will require a hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing scoliosis surgery generally require a hospital stay of 4 to 7 days, depending on the extent of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, monitor for complications, and assist with early mobility.Type of Anesthesia
Scoliosis surgery is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 6 to 8 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for scoliosis surgery involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging and blood work. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The scoliosis surgery procedure typically lasts between 4 to 8 hours, depending on the complexity of the curvature and the surgical technique used. The surgeon will use rods, screws, and bone grafts to correct the spinal curvature and stabilize the spine.Recovery Time
Recovery from scoliosis surgery can take several months. Most patients can begin light activities within 4 to 6 weeks, but full recovery, including the fusion of the spine, may take 6 to 12 months. Physical therapy is often recommended to aid in recovery and improve strength and flexibility.Estimated Cost
The cost of scoliosis surgery can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and rehabilitation.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for scoliosis surgery includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess spinal alignment, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240719143300356544__0.webp)
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS)
- Purpose: To treat various spinal conditions with less tissue disruption and faster recovery.
- Procedure: Small incisions and specialized instruments are used to perform the surgery with minimal impact on surrounding tissues.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the type of spinal condition being treated, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed. In some cases, an overnight stay may be required depending on the complexity of the surgery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing MISS generally do not require a prolonged hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
MISS is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, regional anesthesia with sedation may be used depending on the specific procedure and the patient’s condition.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as pain, swelling, or discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for MISS involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The duration of a MISS procedure typically lasts between 1 to 3 hours, depending on the specific surgery being performed. The surgeon uses small incisions and specialized instruments, often with the assistance of a microscope or endoscope, to address spinal issues such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or spinal fractures with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.Recovery Time
Recovery from MISS is generally quicker than traditional open spine surgery. Most patients can begin light activities within a few days to a week, with full recovery, including the resumption of normal activities, typically occurring within 4 to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting during the recovery period. Physical therapy may be recommended to help restore strength and flexibility.Estimated Cost
The cost of MISS can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and physical therapy.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for MISS includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, increased swelling, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
-for-spinal-pain_20240719143312311676__0.webp)
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Spinal Pain
- Purpose: To reduce chronic back pain by disrupting nerve signals.
- Procedure: Radiofrequency energy is used to heat and destroy the nerve fibers causing pain.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Spinal Pain procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and severity of the pain, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for spinal pain is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing RFA generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from the sedation and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
RFA is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area where the procedure will be done. Sedation may also be provided to help the patient remain comfortable and relaxed during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow for proper recovery and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or swelling.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for RFA involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if sedation is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The RFA procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the number of nerves being treated. During the procedure, the healthcare provider uses radiofrequency energy to heat specific nerve tissues, interrupting pain signals from the spinal area to the brain.Recovery Time
Recovery from RFA is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience temporary discomfort, swelling, or bruising at the treatment site, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. Full pain relief may take several days to weeks to become fully apparent, and the effects can last from several months to over a year.Estimated Cost
The cost of RFA can vary depending on the number of nerves treated, the healthcare provider's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or pain management clinic for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and potential repeat treatments.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for RFA includes monitoring the treatment area for any signs of complications, such as increased pain, swelling, or signs of infection. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions, which may include avoiding strenuous activities for a few days and applying cold packs to reduce swelling. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and to plan any further care if needed.
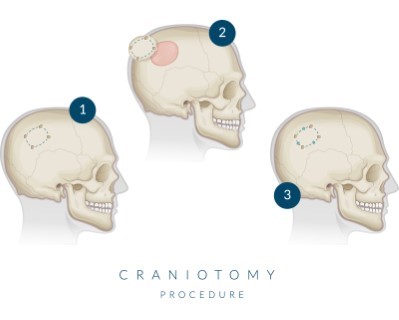
Craniotomy
- Purpose: To access the brain for various procedures including tumor removal, aneurysm clipping, or hematoma evacuation.
- Procedure: A section of the skull is removed to expose the brain; the bone is replaced after the surgery.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Craniotomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and size of the area being operated on, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Craniotomy is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to its complexity and the need for close post-operative monitoring. Most patients will require a hospital stay for recovery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing a craniotomy generally require a hospital stay of 3 to 7 days, depending on the complexity of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, monitor for complications, and provide necessary post-operative care.Type of Anesthesia
Craniotomy is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure. In some cases, a craniotomy may be performed with the patient awake (awake craniotomy) to allow for real-time assessment of brain function.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as swelling, pain, or neurological issues.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for a craniotomy involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging, blood work, and neurological assessments. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The duration of the craniotomy procedure typically lasts between 3 to 8 hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery and the condition being treated. During the procedure, the surgeon temporarily removes a portion of the skull to access the brain, perform the necessary surgery, and then replaces the bone flap.Recovery Time
Recovery from a craniotomy can take several weeks to months. Most patients can begin light activities within 4 to 6 weeks, but full recovery, including the return to normal activities, may take several months. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy may be recommended to aid in recovery, depending on the neurological function affected by the surgery.Estimated Cost
The cost of a craniotomy can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care, rehabilitation, and potential post-operative therapies.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for a craniotomy includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess neurological function, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe headache, increased swelling, or neurological changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
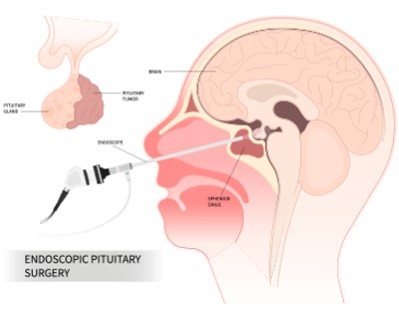
Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery
Purpose: To remove tumors and lesions located at the base of the skull, including pituitary tumors.
Procedure: Minimally invasive surgery performed through the nasal passages using an endoscope.
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the type of condition being treated, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Endoscopic endonasal surgery is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to its complexity and the need for post-operative monitoring. However, in some cases, it may be performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing the patient to return home the same day.
Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing endoscopic endonasal surgery generally require a hospital stay of 1 to 3 days, depending on the complexity of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor for any complications, such as bleeding or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, and to provide necessary post-operative care.
Type of Anesthesia
Endoscopic endonasal surgery is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the procedure.
Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as nasal congestion, headache, or CSF leaks.
Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for endoscopic endonasal surgery involves following specific guidelines from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging studies (MRI, CT scans) and blood work. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.
Procedure Duration
The duration of the endoscopic endonasal surgery procedure typically lasts between 2 to 4 hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery and the condition being treated. The surgeon uses an endoscope, inserted through the nostrils, to access and treat conditions such as pituitary tumors, skull base tumors, and other abnormalities located near the base of the brain.
Recovery Time
Recovery from endoscopic endonasal surgery can vary, but most patients can begin light activities within 1 to 2 weeks. Full recovery, including the resolution of nasal congestion and healing of the surgical site, may take several weeks. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and blowing their nose during the recovery period to prevent complications.
Estimated Cost
The cost of endoscopic endonasal surgery can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care, rehabilitation, and potential post-operative therapies.
Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for endoscopic endonasal surgery includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper healing of the nasal passages and surgical site. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for nasal care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess any changes in neurological function, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe headache, nasal discharge, or neurological changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
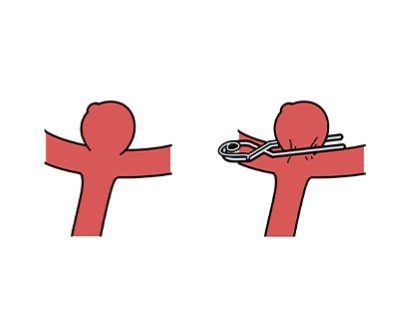
Microsurgical Clipping of Cerebral Aneurysms
Purpose: To treat cerebral aneurysms and prevent rupture.
Procedure: A small clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to isolate it from normal blood circulation.
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Microsurgical Clipping of Cerebral Aneurysms procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and size of the aneurysm, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Microsurgical clipping of cerebral aneurysms is typically performed as an inpatient procedure due to the complexity of the surgery and the need for close post-operative monitoring.
Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing microsurgical clipping generally require a hospital stay of 5 to 10 days, depending on the complexity of the surgery and their overall recovery. This allows healthcare providers to monitor neurological status, manage pain, and prevent complications such as stroke or infection.
Type of Anesthesia
This procedure is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and comfortable during the surgery.
Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as headaches, neurological deficits, or blood clot formation.
Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for microsurgical clipping involves following specific guidelines from the neurosurgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before surgery, and undergoing pre-operative tests like imaging studies (MRI, CT angiography) and blood work. Patients should also arrange for transportation and aftercare following the procedure and ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.
Procedure Duration
The procedure typically lasts between 3 to 6 hours, depending on the location and complexity of the aneurysm. The neurosurgeon accesses the brain through a craniotomy and places a metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent it from rupturing or leaking.
Recovery Time
Recovery from microsurgical clipping can be extensive. Most patients can begin light activities within 4 to 6 weeks, but full recovery, including the return to normal activities, may take several months. Physical therapy and occupational therapy may be recommended to help restore neurological function and improve quality of life after surgery.
Estimated Cost
The cost of microsurgical clipping of cerebral aneurysms can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care, rehabilitation, and potential post-operative therapies.
Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for microsurgical clipping includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper wound healing. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions for wound care, activity restrictions, and gradually increasing mobility. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing, assess neurological function, and address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe headaches, changes in vision, or neurological changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
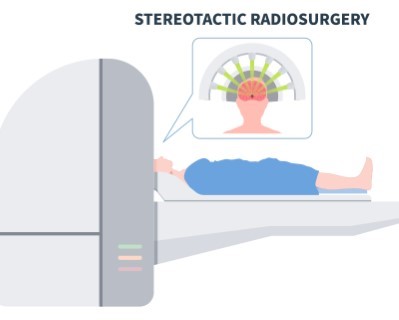
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
Purpose: To treat brain tumors, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and other brain abnormalities without a surgical incision.
Procedure: High doses of targeted radiation are delivered to the abnormal tissue while sparing surrounding healthy tissue.
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Gamma Knife Radiosurgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the location and size of the target area, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Gamma Knife radiosurgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.
Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing Gamma Knife radiosurgery generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from the treatment and are stable.
Type of Anesthesia
Gamma Knife radiosurgery is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation. The patient is awake during the procedure, but the scalp is numbed to prevent discomfort during the head frame placement. In some cases, light sedation may be offered to help the patient remain calm and comfortable.
Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow for proper recovery and to monitor for any potential side effects, such as headaches or nausea.
Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for Gamma Knife radiosurgery involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, fasting before the procedure if sedation is used, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.
Procedure Duration
The Gamma Knife procedure typically lasts between 1 to 4 hours, depending on the complexity of the treatment plan. During the procedure, multiple focused beams of radiation are directed at the target area, such as a brain tumor or arteriovenous malformation (AVM), to destroy abnormal cells without harming surrounding healthy tissue.
Recovery Time
Recovery from Gamma Knife radiosurgery is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day or two. Some patients may experience temporary side effects, such as mild headaches, nausea, or fatigue, but these symptoms usually resolve within a few days. The full effects of the treatment may take weeks to months to become apparent as the treated area gradually shrinks or stabilizes.
Estimated Cost
The cost of Gamma Knife radiosurgery can vary depending on the complexity of the treatment, the condition being treated, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and imaging studies to monitor the results of the treatment.
Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for Gamma Knife radiosurgery includes monitoring for any side effects and following up with the healthcare provider to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. Patients may need to undergo periodic imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, to track the progress of the treated area. Any signs of complications, such as persistent headaches, seizures, or neurological changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
