Ophthalmology Treatments
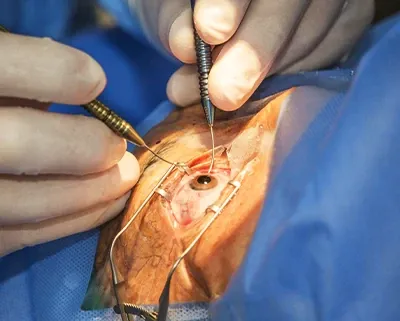
Cataract Surgery
Purpose: Removes cloudy lens to restore clear vision.
Procedure: The cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Cataract Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s overall eye health, the severity of the cataract, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Cataract surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.
Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing cataract surgery generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged within a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from the effects of sedation or anesthesia.
Type of Anesthesia
Cataract surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia, often combined with sedation to keep the patient comfortable and relaxed. The eye is numbed so the patient does not feel pain during the procedure.
Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection or changes in vision.
Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for cataract surgery involves following specific instructions from the healthcare provider, such as using prescribed eye drops before the surgery, fasting if sedation is planned, and adjusting medications as needed. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.
Procedure Duration
The cataract surgery procedure typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes. During the surgery, the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore clear vision.
Recovery Time
Recovery from cataract surgery is generally quick, with most patients noticing an improvement in vision within a few days. Full recovery typically takes about 4 to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes, heavy lifting, and strenuous activities during the recovery period to ensure proper healing.
Estimated Cost
The cost of cataract surgery can vary depending on the type of intraocular lens used, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.
Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for cataract surgery includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation, protecting the eye with a shield, and avoiding activities that could strain the eyes. Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and assess the success of the surgery. Any signs of complications, such as increased pain, redness, or vision changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240719160453970932__0.webp)
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis)
- Purpose: Corrects refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
- Procedure: A laser reshapes the cornea to improve vision.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard LASIK procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s eye health, the degree of refractive error, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
LASIK is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing LASIK do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged within a couple of hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have recovered from any sedation used during the surgery.Type of Anesthesia
LASIK is performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to help the patient stay relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least a week after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as dry eyes or vision fluctuations.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for LASIK involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as discontinuing the use of contact lenses for a period before surgery, avoiding makeup or lotions around the eyes, and arranging for someone to drive the patient home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The LASIK procedure typically lasts about 15 to 30 minutes for both eyes. During the surgery, the surgeon creates a thin flap in the cornea and reshapes the underlying tissue using a laser to correct vision.Recovery Time
Recovery from LASIK is generally quick, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in vision within 24 hours. Full stabilization of vision can take a few weeks to a few months. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes, swimming, and strenuous activities during the initial recovery period to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of LASIK can vary depending on the surgeon's expertise, the technology used, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and enhancement procedures if needed.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for LASIK includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation, protecting the eyes from bright light, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process. Any signs of complications, such as severe dry eyes, halos around lights, or fluctuating vision, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240719160824011408__0.webp)
PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy)
- Purpose: Corrects refractive errors by reshaping the cornea.
- Procedure: The corneal surface layer is removed, and a laser reshapes the underlying corneal tissue.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard PRK procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s eye health, the degree of refractive error, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
PRK is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing PRK do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received instructions for post-operative care.Type of Anesthesia
PRK is performed under local anesthesia using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to help the patient remain calm and relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least a week after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or vision fluctuations.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for PRK involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as discontinuing the use of contact lenses for a period before surgery, avoiding makeup or lotions around the eyes, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The PRK procedure typically lasts about 15 to 30 minutes for both eyes. During the surgery, the surgeon removes the outer layer of the cornea (epithelium) and uses a laser to reshape the corneal tissue underneath to correct vision.Recovery Time
Recovery from PRK is generally slower than LASIK, with most patients experiencing an improvement in vision within a few days, but full stabilization can take several weeks to a few months. Patients may experience discomfort or sensitivity to light during the initial recovery period and should avoid rubbing their eyes, swimming, and strenuous activities.Estimated Cost
The cost of PRK can vary depending on the surgeon's expertise, the technology used, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and enhancement procedures if needed.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for PRK includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Patients should also wear protective eyewear and avoid exposure to bright lights. Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the healing process and ensure optimal results. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, prolonged blurry vision, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
_20240719161208428308__0.webp)
SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction)
- Purpose: Corrects myopia and astigmatism by removing a small piece of corneal tissue.
- Procedure: A laser creates and removes a lenticule through a small incision in the cornea.
Note: The information provided here applies to standard SMILE procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s eye health, the degree of refractive error, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
SMILE is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing SMILE do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged within a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-operative care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
SMILE is performed under local anesthesia using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to help the patient remain relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least a week after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or vision fluctuations.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for SMILE involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as discontinuing the use of contact lenses for a period before surgery, avoiding makeup or lotions around the eyes, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The SMILE procedure typically lasts about 10 to 20 minutes for both eyes. During the surgery, a femtosecond laser is used to create a small, lens-shaped piece of tissue (lenticule) within the cornea, which is then removed through a small incision to reshape the cornea and correct vision.Recovery Time
Recovery from SMILE is generally quicker than PRK and comparable to LASIK, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in vision within a few days. Full stabilization of vision can take several weeks. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes, swimming, and engaging in strenuous activities during the initial recovery period to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of SMILE can vary depending on the surgeon's expertise, the technology used, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and enhancement procedures if needed.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for SMILE includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Patients should also wear protective eyewear and avoid exposure to bright lights. Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the healing process and ensure optimal results. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, prolonged blurry vision, or signs of infection, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.

Glaucoma Surgery
- Purpose: Reduces intraocular pressure to prevent damage to the optic nerve.
- Procedure: Various techniques including trabeculectomy, laser trabeculoplasty, and shunt implants.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Glaucoma Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the type of glaucoma, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Glaucoma surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed. However, some types of glaucoma surgery may require a short hospital stay for observation.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing glaucoma surgery generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-operative care instructions. In more complex cases, an overnight stay may be recommended.Type of Anesthesia
Glaucoma surgery is commonly performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may also be used to help the patient stay relaxed. In certain cases, general anesthesia may be required, particularly for more complex surgeries.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as increased eye pressure or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for glaucoma surgery involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before the surgery, fasting if sedation or general anesthesia is planned, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The duration of glaucoma surgery varies depending on the type of procedure being performed, but it typically lasts between 30 minutes to 2 hours. Common glaucoma surgeries include trabeculectomy, laser trabeculoplasty, and the insertion of drainage devices to lower intraocular pressure.Recovery Time
Recovery from glaucoma surgery can take several weeks, with most patients experiencing an improvement in eye pressure within a few days. Full recovery and stabilization of vision may take 4 to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes, strenuous activities, and exposure to bright lights during the initial recovery period to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of glaucoma surgery can vary depending on the type of surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for glaucoma surgery includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and manage eye pressure. Patients should attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing and the effectiveness of the surgery. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, or changes in vision, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
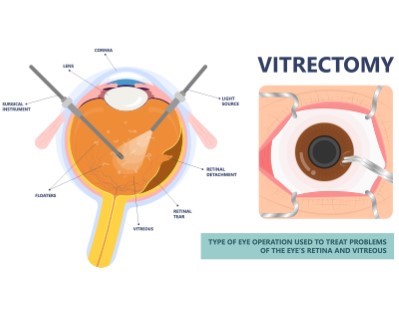
Vitrectomy
- Purpose: Removes the vitreous gel from the eye to treat conditions like retinal detachment, macular hole, or vitreous hemorrhage.
- Procedure: The vitreous gel is removed and replaced with a saline solution.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Vitrectomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the underlying eye condition being treated, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Vitrectomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed. However, in more complex cases, an overnight hospital stay may be required.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing vitrectomy generally do not require a prolonged hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and their condition is stable. In cases of extensive surgery or complications, a 1-day hospital stay may be necessary.Type of Anesthesia
Vitrectomy is commonly performed under local anesthesia with sedation, ensuring the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, particularly for more complex or prolonged surgeries.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as increased eye pressure or infection. In cases where a gas bubble is used in the eye during surgery, air travel is contraindicated until the bubble has completely absorbed.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for vitrectomy involves following specific guidelines from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before surgery, fasting if sedation or general anesthesia is planned, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The duration of a vitrectomy can vary depending on the condition being treated and the complexity of the case, but it typically lasts between 1 to 3 hours. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the vitreous gel from the eye and may perform additional repairs, such as retinal detachment repair or the removal of scar tissue.Recovery Time
Recovery from vitrectomy can take several weeks to a few months, depending on the extent of the surgery and the underlying condition. Patients may need to maintain specific head positions if a gas bubble was used during surgery. Full stabilization of vision may take time, and patients should avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and sudden head movements during the initial recovery period.Estimated Cost
The cost of vitrectomy can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for vitrectomy includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and manage eye pressure. Patients should attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing and the effectiveness of the surgery. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, or vision changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately. If a gas bubble was used, patients should follow specific instructions regarding head positioning and avoid air travel until cleared by their ophthalmologist.
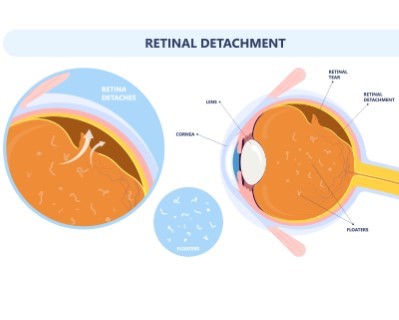
Retinal Detachment Surgery
- Purpose: Reattaches the retina to prevent vision loss.
- Procedure: Techniques include pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckle, and vitrectomy.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Retinal Detachment Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the detachment, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this procedure through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Retinal detachment surgery can be performed as either an inpatient or outpatient procedure, depending on the complexity of the detachment and the specific surgical method used.Hospital Stay Duration
For less complex cases, patients may be discharged the same day after the surgery. However, more complex surgeries may require an overnight hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation, ensuring the patient is comfortable and pain-free. In more complex cases, general anesthesia may be required.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 2 to 4 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as increased eye pressure or recurrence of the detachment. If a gas bubble is used in the eye during surgery, air travel is contraindicated until the bubble has fully absorbed.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for retinal detachment surgery involves following specific guidelines from the ophthalmologist, such as fasting before surgery if sedation or general anesthesia is planned, using prescribed eye drops, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The duration of retinal detachment surgery varies depending on the severity of the detachment and the method used but generally lasts between 1 to 3 hours. Surgical techniques may include scleral buckling, vitrectomy, or pneumatic retinopexy, depending on the specific needs of the patient.Recovery Time
Recovery from retinal detachment surgery can take several weeks to a few months. During the initial recovery period, patients may need to maintain specific head positions, especially if a gas bubble was used during surgery. Full stabilization of vision can take time, and patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sudden head movements during recovery.Estimated Cost
The cost of retinal detachment surgery can vary based on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for retinal detachment surgery includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and manage eye pressure. Patients must adhere to all post-surgery instructions, including maintaining specific head positions if a gas bubble was used. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and ensure the retina remains attached. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, vision changes, or signs of detachment recurrence, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately. Air travel is strictly prohibited if a gas bubble was used until it has completely absorbed, which can take several weeks.
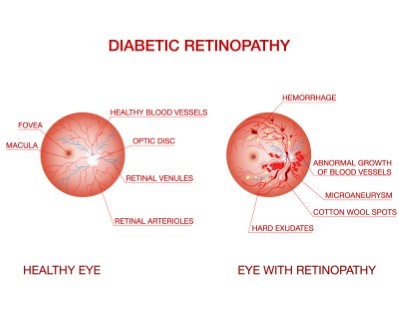
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
- Purpose: Treats damage to the retina caused by diabetes.
- Procedure: Includes laser treatment (photocoagulation) and vitrectomy.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the retinopathy, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Diabetic retinopathy treatment is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing treatment for diabetic retinopathy generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
Most treatments for diabetic retinopathy, such as laser therapy or injections, are performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to help the patient remain calm and relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least a few days after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as changes in vision or eye discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for diabetic retinopathy treatment involves following specific guidelines from the ophthalmologist, such as managing blood sugar levels, using prescribed eye drops, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The duration of diabetic retinopathy treatment varies depending on the type of procedure being performed. Laser treatments typically last about 20 to 30 minutes, while injections or other interventions may take less time. In some cases, multiple sessions may be required.Recovery Time
Recovery from diabetic retinopathy treatment is generally quick, with most patients experiencing minimal downtime. However, vision may be blurry for a few hours to days after the procedure, and patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and exposure to bright lights during the initial recovery period.Estimated Cost
The cost of diabetic retinopathy treatment can vary depending on the type of procedure, the frequency of treatments, the ophthalmologist's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for diabetic retinopathy treatment includes using prescribed eye drops to reduce inflammation and prevent infection, monitoring blood sugar levels, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment. Patients should avoid activities that could strain their eyes and should report any signs of complications, such as increased pain, redness, or changes in vision, to their healthcare provider immediately.
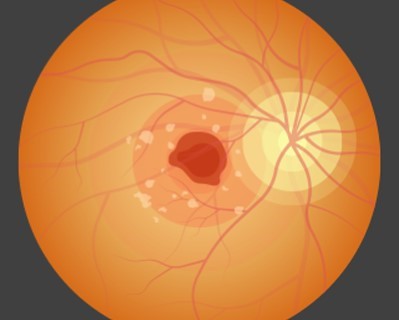
Macular Degeneration Treatment
- Purpose: Treats age-related macular degeneration to slow vision loss.
- Procedure: Includes anti-VEGF injections, laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Macular Degeneration Treatment procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the type and severity of macular degeneration, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after treatment. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Macular degeneration treatment is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing treatment for macular degeneration generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
Most treatments for macular degeneration, such as injections or laser therapy, are performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to help the patient remain calm and relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least a few days after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as changes in vision or eye discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for macular degeneration treatment involves following specific guidelines from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops, managing underlying health conditions, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The duration of macular degeneration treatment varies depending on the type of procedure being performed. Injections to treat wet macular degeneration typically take a few minutes, while laser treatments may last 20 to 30 minutes. Multiple sessions may be required depending on the patient's condition.Recovery Time
Recovery from macular degeneration treatment is generally quick, with most patients experiencing minimal downtime. Vision may be blurry or slightly altered for a few hours to days after the procedure. Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and exposure to bright lights during the initial recovery period to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of macular degeneration treatment can vary depending on the type of procedure, the frequency of treatments, the ophthalmologist's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for macular degeneration treatment includes using prescribed eye drops to reduce inflammation and prevent infection, monitoring vision changes, and attending regular follow-up appointments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. Patients should avoid activities that could strain their eyes and should report any signs of complications, such as increased pain, redness, or further changes in vision, to their healthcare provider immediately.
_20240719162521897117__0.webp)
Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Purpose: Corrects droopy eyelids and removes excess skin and fat.
- Procedure: Incisions are made along the eyelid creases to remove or reposition tissues.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Blepharoplasty procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the extent of the surgery, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Blepharoplasty is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing blepharoplasty generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and are stable.Type of Anesthesia
Blepharoplasty is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation to keep the patient comfortable. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the extent of the surgery and the patient’s preference.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as swelling or bruising.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for blepharoplasty involves following specific instructions from the surgeon, such as avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, arranging for transportation home after the procedure, and ensuring that all necessary medical documentation is available if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The blepharoplasty procedure typically lasts between 1 to 3 hours, depending on whether the upper eyelids, lower eyelids, or both are being treated. The surgeon removes or repositions excess skin, muscle, and fat to achieve the desired aesthetic or functional result.Recovery Time
Recovery from blepharoplasty is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a few days. Swelling and bruising typically subside within 1 to 2 weeks. Full recovery may take several weeks, during which patients should avoid strenuous activities, bending over, and wearing contact lenses.Estimated Cost
The cost of blepharoplasty can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for blepharoplasty includes managing swelling and discomfort with cold compresses, keeping the head elevated, and using prescribed eye drops or ointments. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions carefully and attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing and ensure optimal results. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, excessive swelling, or changes in vision, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
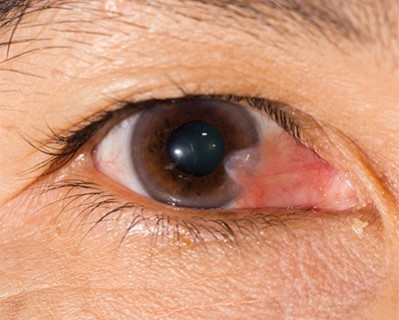
Pterygium Surgery
- Purpose: Removes a pterygium, a benign growth on the conjunctiva.
- Procedure: The growth is surgically removed, and the area may be covered with a graft.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Pterygium Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the size and location of the pterygium, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Pterygium surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing pterygium surgery generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and their condition is stable.Type of Anesthesia
Pterygium surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia with numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be provided to help the patient remain calm and relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection or recurrence of the pterygium.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for pterygium surgery involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as discontinuing the use of contact lenses, avoiding certain medications that can increase bleeding, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The pterygium surgery procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to 1 hour. During the surgery, the surgeon removes the pterygium—a benign growth of the conjunctiva—and may use a graft from the patient’s own conjunctiva or amniotic membrane to cover the affected area and reduce the risk of recurrence.Recovery Time
Recovery from pterygium surgery is generally quick, with most patients able to resume light activities within a few days. However, full healing may take several weeks. During this time, patients should avoid exposure to bright sunlight, wind, and dust, as well as strenuous activities that could strain the eyes.Estimated Cost
The cost of pterygium surgery can vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for pterygium surgery includes using prescribed eye drops to reduce inflammation, prevent infection, and promote healing. Patients should protect their eyes from environmental irritants by wearing sunglasses and following their surgeon’s instructions for activity restrictions. Regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and check for signs of recurrence. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, or vision changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
Keratoconus Treatment
- Purpose: Treats keratoconus, a condition where the cornea thins and bulges outward.
- Procedure: Includes corneal cross-linking, Intacs, and corneal transplant.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Keratoconus Treatment procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the keratoconus, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after treatment. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Keratoconus treatment is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing keratoconus treatment generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
Most keratoconus treatments, such as corneal cross-linking or intacs insertion, are performed under local anesthesia with numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may be offered to help the patient remain calm and relaxed.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least a few days to a week after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as discomfort or changes in vision.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for keratoconus treatment involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as discontinuing the use of contact lenses for a period before treatment, using prescribed eye drops, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the treatment.Procedure Duration
The duration of keratoconus treatment varies depending on the type of procedure being performed. Corneal cross-linking typically lasts about 1 to 2 hours, while intacs insertion or other surgical interventions may take longer. Multiple sessions may be required depending on the treatment plan.Recovery Time
Recovery from keratoconus treatment is generally quick, with most patients experiencing improvement in vision within a few days to weeks, depending on the treatment. Full stabilization of vision may take several months. During the initial recovery period, patients should avoid strenuous activities, exposure to bright lights, and wearing contact lenses until cleared by their ophthalmologist.Estimated Cost
The cost of keratoconus treatment can vary depending on the type of procedure, the frequency of treatments, the ophthalmologist's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their ophthalmologist or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for keratoconus treatment includes using prescribed eye drops to reduce inflammation, prevent infection, and promote healing. Patients should attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and to adjust the treatment plan as needed. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, or vision changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
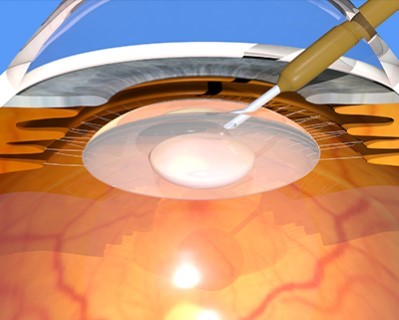
Cataract Phacoemulsification
- Purpose: Removes cataracts using ultrasound waves to break up the lens.
- Procedure: The lens fragments are suctioned out and replaced with an artificial lens.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Cataract Phacoemulsification procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s overall eye health, the density of the cataract, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Cataract phacoemulsification is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing cataract phacoemulsification do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged within a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have recovered from any sedation or anesthesia.Type of Anesthesia
Cataract phacoemulsification is performed under local anesthesia, often using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Sedation may also be offered to help the patient stay relaxed and comfortable.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection or changes in vision.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for cataract phacoemulsification involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before surgery, fasting if sedation is planned, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The cataract phacoemulsification procedure typically lasts between 15 to 30 minutes. During the surgery, the cloudy lens is emulsified using ultrasonic energy and then removed. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is then inserted to restore clear vision.Recovery Time
Recovery from cataract phacoemulsification is generally quick, with most patients noticing an improvement in vision within a few days. Full recovery and stabilization of vision typically take about 4 to 6 weeks. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes, heavy lifting, and strenuous activities during the recovery period to ensure proper healing.Estimated Cost
The cost of cataract phacoemulsification can vary depending on the type of intraocular lens used, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for cataract phacoemulsification includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Patients should protect their eyes from bright light and avoid activities that could strain their eyes. Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and assess the success of the surgery. Any signs of complications, such as increased pain, redness, or vision changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
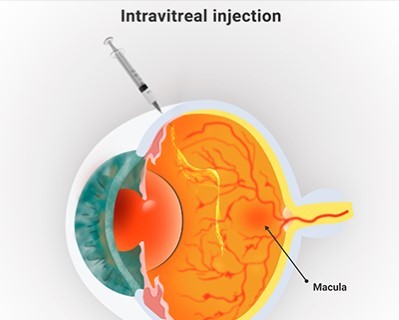
Intravitreal Injections
- Purpose: Delivers medication directly into the eye to treat various retinal conditions.
- Procedure: A fine needle is used to inject medication into the vitreous cavity.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Intravitreal Injection procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s underlying eye condition, the type of medication being administered, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Intravitreal injections are typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing intravitreal injections do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
Intravitreal injections are performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. The procedure is generally quick and minimally invasive.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow for proper monitoring and to address any potential complications, such as eye discomfort or vision changes.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for intravitreal injections involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before the procedure, and arranging for transportation home after the treatment. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The intravitreal injection procedure typically lasts just a few minutes. The medication is injected directly into the vitreous humor, the gel-like substance inside the eye, to treat conditions such as macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, or retinal vein occlusion.Recovery Time
Recovery from intravitreal injections is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, redness, or blurred vision immediately following the injection, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days.Estimated Cost
The cost of intravitreal injections can vary depending on the type of medication used, the frequency of treatments, the ophthalmologist's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for intravitreal injections includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Patients should monitor for any signs of complications, such as increased pain, severe redness, or changes in vision, and report these to their healthcare provider immediately. Regular follow-up appointments are important to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and determine the need for additional injections.

Pediatric Strabismus Surgery
- Purpose: Corrects misalignment of the eyes in children.
- Procedure: The muscles controlling eye movement are repositioned.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Pediatric Strabismus Surgery procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the strabismus, the child’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Parents seeking this surgery for their child through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Pediatric strabismus surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most children to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Children undergoing strabismus surgery generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once they have recovered from anesthesia and their condition is stable.Type of Anesthesia
Strabismus surgery is performed under general anesthesia to ensure the child is fully asleep and pain-free during the procedure. This helps keep the child comfortable and still during the surgery.Travel After Procedure
Parents are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection or changes in eye alignment.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for pediatric strabismus surgery involves following specific instructions from the healthcare provider, such as fasting before surgery, adjusting medications, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Parents should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The strabismus surgery procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the surgery, the surgeon adjusts the position or tension of the eye muscles to correct the misalignment of the eyes.Recovery Time
Recovery from strabismus surgery is generally quick, with most children resuming light activities within a few days. The eyes may appear red or swollen, and there may be some discomfort for a few days after the procedure. Full recovery typically takes 1 to 2 weeks, during which parents should follow the surgeon’s instructions regarding activity restrictions and eye care.Estimated Cost
The cost of pediatric strabismus surgery can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Parents should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for pediatric strabismus surgery includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Parents should ensure that their child avoids rubbing their eyes and adheres to any activity restrictions provided by the surgeon. Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the success of the surgery and to address any concerns. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, excessive redness, or significant changes in eye alignment, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
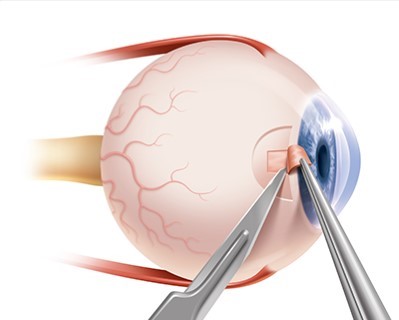
Canaloplasty
- Purpose: Treats glaucoma by improving the drainage of the eye's fluid.
- Procedure: A microcatheter is inserted into the eye's drainage canal to enlarge it.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Canaloplasty procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the severity of the patient’s glaucoma, overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Canaloplasty is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the surgery is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing canaloplasty generally do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged a few hours after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have recovered from anesthesia.Type of Anesthesia
Canaloplasty is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's preference.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as increased eye pressure or infection.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for canaloplasty involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before surgery, fasting if sedation or general anesthesia is planned, and arranging for transportation home after the procedure. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The canaloplasty procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the surgery, the surgeon creates a small incision to access the Schlemm’s canal and then inserts a microcatheter to enlarge the canal, helping to improve the drainage of intraocular fluid and reduce eye pressure.Recovery Time
Recovery from canaloplasty is generally quick, with most patients experiencing a reduction in eye pressure within a few days to weeks. Full recovery may take a few weeks, during which patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and any activities that could strain the eyes.Estimated Cost
The cost of canaloplasty can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for canaloplasty includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection, reduce inflammation, and manage eye pressure. Patients should attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing and the effectiveness of the surgery. Any signs of complications, such as severe pain, redness, or vision changes, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately. It is also important to avoid rubbing the eyes or engaging in activities that could increase eye pressure during the recovery period.
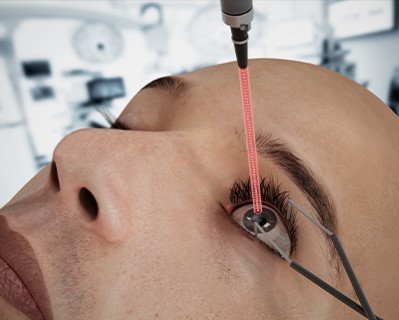
Photocoagulation
- Purpose: Treats various retinal disorders by sealing or destroying abnormal blood vessels.
- Procedure: A laser is used to create small burns on the retina.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Photocoagulation procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the underlying eye condition being treated, the patient’s overall eye health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Photocoagulation is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing photocoagulation do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
Photocoagulation is performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. The procedure is generally quick and minimally invasive.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow for proper monitoring and to address any potential complications, such as eye discomfort or vision changes.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for photocoagulation involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before the procedure, and arranging for transportation home after the treatment. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The photocoagulation procedure typically lasts about 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the extent of treatment needed. The ophthalmologist uses a laser to create small burns on the retina, which helps to seal leaking blood vessels or reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in conditions such as diabetic retinopathy.Recovery Time
Recovery from photocoagulation is generally quick, with most patients able to resume normal activities within a day. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, redness, or blurred vision immediately following the procedure, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days.Estimated Cost
The cost of photocoagulation can vary depending on the extent of treatment, the ophthalmologist's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for photocoagulation includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Patients should monitor for any signs of complications, such as increased pain, severe redness, or changes in vision, and report these to their healthcare provider immediately. Regular follow-up appointments are important to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and determine if additional sessions are needed.

YAG Laser Capsulotomy
- Purpose: Treats clouding of the lens capsule after cataract surgery.
- Procedure: A laser is used to create an opening in the cloudy capsule.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard YAG Laser Capsulotomy procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the patient’s overall eye health and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this treatment through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
YAG laser capsulotomy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing most patients to return home the same day after the treatment is completed.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing YAG laser capsulotomy do not require a hospital stay. They are usually discharged shortly after the procedure, once their eyes have been checked and they have received post-treatment care instructions.Type of Anesthesia
YAG laser capsulotomy is performed under local anesthesia, using numbing eye drops to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. The procedure is non-invasive and generally well-tolerated.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 24 to 48 hours after the procedure to allow for proper monitoring and to address any potential complications, such as temporary vision changes or eye discomfort.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for YAG laser capsulotomy involves following specific instructions from the ophthalmologist, such as using prescribed eye drops before the procedure, and arranging for transportation home after the treatment. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the procedure.Procedure Duration
The YAG laser capsulotomy procedure typically lasts about 10 to 20 minutes. During the procedure, the ophthalmologist uses a laser to create a small opening in the cloudy posterior capsule that can form after cataract surgery, improving the patient’s vision.Recovery Time
Recovery from YAG laser capsulotomy is generally quick, with most patients experiencing an improvement in vision within a few hours to a day after the procedure. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or floaters in their vision, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days.Estimated Cost
The cost of YAG laser capsulotomy can vary depending on the ophthalmologist's expertise and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or treatment center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for follow-up care and medications.Post-procedure Care
Post-procedure care for YAG laser capsulotomy includes using prescribed eye drops to prevent inflammation and monitoring for any signs of complications, such as increased pain, severe redness, or changes in vision. Patients should attend follow-up appointments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and to ensure the eye is healing properly. Any persistent symptoms or concerns should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
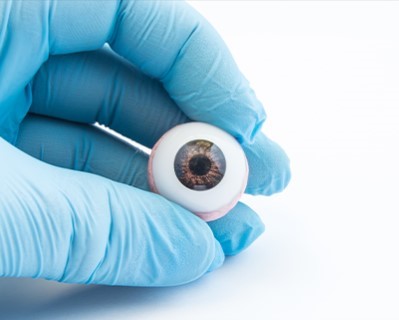
Enucleation
- Purpose: Removes a damaged or diseased eye.
- Procedure: The eye is surgically removed, often replaced with an ocular prosthesis.
-
Note: The information provided here applies to standard Enucleation procedures under typical conditions. However, specifics may vary based on individual factors, such as the underlying reason for enucleation, the patient’s overall health, and any complications that might arise during or after the procedure. Patients seeking this surgery through health tourism should also consider local regulations and the importance of choosing a reputable clinic that adheres to international standards.
Inpatient/Outpatient
Enucleation is typically performed as an inpatient procedure, requiring a hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery after the surgery.Hospital Stay Duration
Patients undergoing enucleation generally require a hospital stay of 1 to 2 days to ensure proper post-operative care and monitoring. This allows healthcare providers to manage pain, prevent infection, and monitor for any complications.Type of Anesthesia
Enucleation is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is fully unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.Travel After Procedure
Patients are generally advised to avoid long-distance travel for at least 2 to 4 weeks after the procedure to allow for proper healing and to monitor for any potential complications, such as infection or issues with the eye socket.Pre-procedure Preparation
Preparation for enucleation involves following specific guidelines from the healthcare provider, such as fasting before surgery, adjusting medications, and undergoing pre-operative tests like blood work and imaging. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation and medical records if traveling internationally for the surgery.Procedure Duration
The enucleation procedure typically lasts between 1 to 2 hours. During the surgery, the entire eye is removed, and an orbital implant is usually placed in the eye socket to maintain its shape. A temporary conformer is often placed over the implant to aid in healing and to prepare for a future prosthetic eye.Recovery Time
Recovery from enucleation takes several weeks. Patients may experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort around the eye socket, which should gradually improve. Full healing typically occurs within 4 to 6 weeks, after which a custom prosthetic eye can be fitted. Patients should avoid strenuous activities and follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for eye socket care during recovery.Estimated Cost
The cost of enucleation can vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's expertise, and geographic location. Patients should consult their healthcare provider or surgical center for detailed cost information, including any additional fees for the orbital implant, prosthetic eye, and follow-up care.Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care for enucleation includes managing pain, preventing infection, and ensuring proper healing of the eye socket. Patients will need to use prescribed medications and follow specific instructions for cleaning the socket and caring for the implant. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing and prepare for the fitting of a prosthetic eye. Any signs of complications, such as increased pain, discharge, or swelling, should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately.
